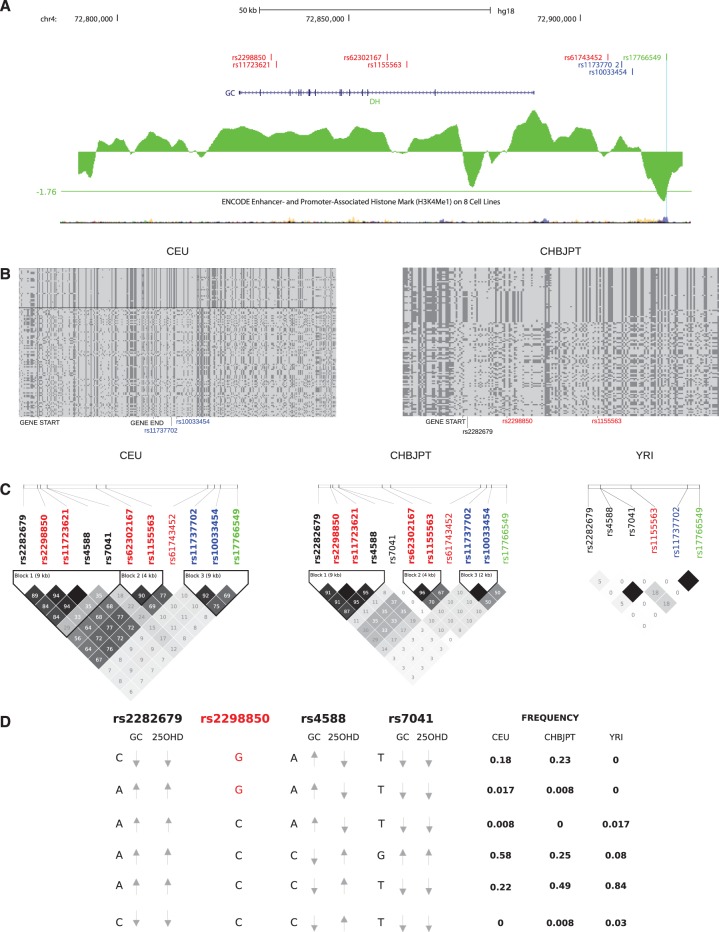
Fig. 4.—
Natural selection at GC in human populations. (A) Schematic representation of GC within the UCSC Genome Browser view. The location of the selection targets and of the GWAS variant are also shown, together with relevant ENCODE tracks. Variants are color coded by population: YRI, green; CEU, blue; CHBJPT, red. A sliding-window analysis of normalized DH is also shown for YRI; the horizontal line represents the fifth percentile in the distribution of DH values. (B) Schematic representation of CEU (left) and CHBJPT (right) haplotypes for genomic regions centered around the selected variants. Each line represents a haplotype, columns indicate polymorphic positions. Dark gray, derived alleles; light gray, ancestral alleles. The thick horizontal line separates haplotypes carrying the ancestral (bottom) and derived (top) allele. (C) LD plot (r2) for the selected targets in the three populations, the GWAS variant, and two nonsynonymous SNPs in GC (see text). Variants are color coded as in (A). (D) Schematic representation of the major human haplotypes for rs2283679, rs2298850, rs4588, and rs7041. Arrows indicate the association with increased or decreased levels of vitamin D-binding protein (GC) and 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25ODH). The selected allele in CHBJPT for rs2298850 is colored in red. The frequency for each haplotype in the three populations is also reported.