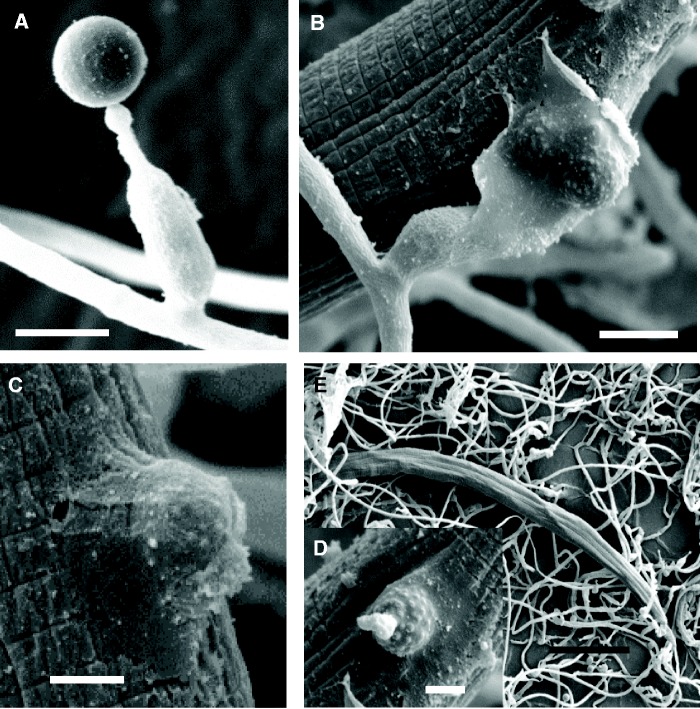
Fig. 1.—
Conidia and the infection stages of Hirsutella minnesotensis on SCN. (A) Conidium of H. minnesotensis. (B, C) A conidium adhered to the cuticle of a passby nematode by secretion of adhesive substances. (D) The cuticle of nematode was degraded and penetrated by an adhesive conidium. (E) The fungus grew in the body of the nematode. Bars: 5.0 μm for (A) and (B), 2.5 μm for (C) and (D), and 50.0 μm for (E).