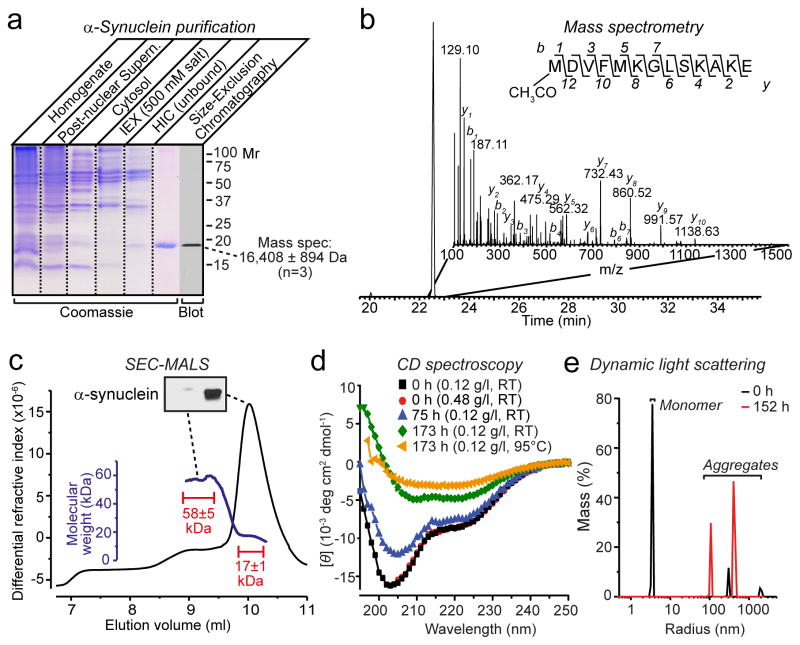
Figure 2.
a, SDS-PAGE analysis of five stages of α-synuclein purification from mouse brain (IEX, anion exchange chromatography, HIC, hydrophobic interaction chromatography). Purified α-synuclein was also analyzed by immunoblotting and mass spectrometry as shown.
b, Mass spectrometry analysis reveals N-terminal acetylation of native α-synuclein. Shown is an extracted ion chromatogram of the N-terminally acetylated α-synuclein peptide (inset: MSMS spectrum containing the sequence of the N-terminal peptide and identified b and y ions).
c, SEC-MALS shows that purified brain α-synuclein (150 μg) is largely monomeric (main peak with a mass of 17±1 kDa), but includes a minor component (plateau along the left shoulder with a mass of 58±5 kDa) that contains little detectable α-synuclein (see immunoblot in insert). Calculated masses were extracted from marked areas.
d, CD spectroscopy of freshly purified brain α-synuclein (7.5 μM) shows mainly disordered conformations that progressively acquire structured conformations as a result of time- and temperature-dependent aggregation.
e, Purified brain α-synuclein (0.12 mg/ml) rapidly aggregates as measured by dynamic light scattering immediately (0 h) or 152 h after purification.