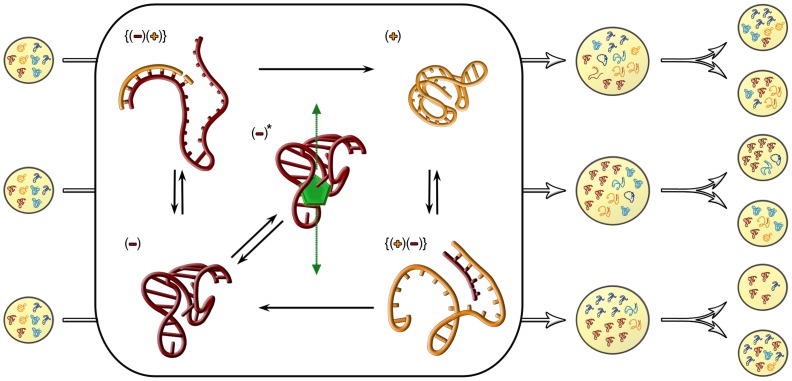
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the main reactions and components of vesicles with complementary replicating strands.
Vesicles are composed of two types of macromolecules (type 1 as red, and type 2 as blue), and with two strand types (plus ( ) strands with light, and minus (
) strands with light, and minus ( ) strands with dark shading). The minus (
) strands with dark shading). The minus ( ) strands (molecules colored dark red) serve both as enzymes (enzymatic activity indicated with asterisk) for producing monomers (molecule colored green) from source material, and as templates for producing plus (
) strands (molecules colored dark red) serve both as enzymes (enzymatic activity indicated with asterisk) for producing monomers (molecule colored green) from source material, and as templates for producing plus ( ) strands (molecules colored orange). The monomers are used as the building blocks (green arrow) for the productions of replicators (replication complexes are indicated in curly brackets). The plus strand only serves as template for producing minus strands. For molecule type 2, the metabolic and replication processes are similar to those of molecule type 1 described above, except that the minus (
) strands (molecules colored orange). The monomers are used as the building blocks (green arrow) for the productions of replicators (replication complexes are indicated in curly brackets). The plus strand only serves as template for producing minus strands. For molecule type 2, the metabolic and replication processes are similar to those of molecule type 1 described above, except that the minus ( ) strand catalyzes a different chemical reaction.
) strand catalyzes a different chemical reaction.