Figure 4. Factors affecting the rate of asymmetry between the minus and the plus strands.
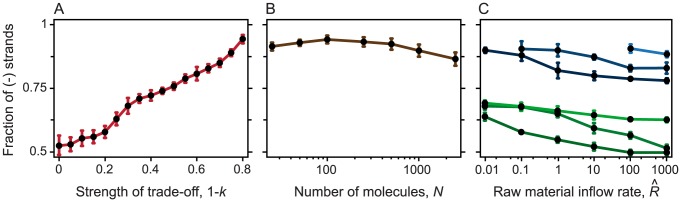
(A) In cases when the strength of trade-off is high (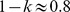 ), the asymmetry between the minus and plus strands is strong, however as the strength of trade-off decreases (
), the asymmetry between the minus and plus strands is strong, however as the strength of trade-off decreases (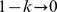 ), since in these cases molecules can achieve high metabolic activity without trading off their replication affinities, the asymmetry becomes less pronounced. (B) As the number of the initial number of molecules (
), since in these cases molecules can achieve high metabolic activity without trading off their replication affinities, the asymmetry becomes less pronounced. (B) As the number of the initial number of molecules (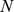 ) per vesicle is increased (
) per vesicle is increased (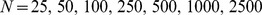 ) the rate of asymmetry gradually decreases (
) the rate of asymmetry gradually decreases (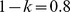 ). (C) The effect of kinetic parameters for strong trade-off (blue lines:
). (C) The effect of kinetic parameters for strong trade-off (blue lines: 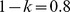 ) and for weak trade-off (green lines:
) and for weak trade-off (green lines: 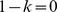 ). Here we increased the inflow rate of source material from the environment into the vesicle (
). Here we increased the inflow rate of source material from the environment into the vesicle (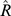 ) (light blue and green lines:
) (light blue and green lines: 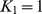 and
and 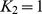 ; middle dark blue and green lines:
; middle dark blue and green lines: 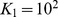 and
and 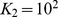 ; dark blue and green lines:
; dark blue and green lines: 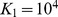 and
and 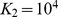 ). For low inflow rate and kinetic constants, high metabolic activities of minus strands evolve, which results in high rate of asymmetries between the two strands. However lowering the inflow rate or the kinetic rate of reactions beyond a threshold results in the extinction of replicators (notice the absence of equilibrium ratio of asymmetry, for example
). For low inflow rate and kinetic constants, high metabolic activities of minus strands evolve, which results in high rate of asymmetries between the two strands. However lowering the inflow rate or the kinetic rate of reactions beyond a threshold results in the extinction of replicators (notice the absence of equilibrium ratio of asymmetry, for example  ,
, 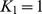 and
and 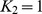 , i.e. left hand side of the light blue curve). The results are averaged over 5 replicate model runs, and over 1,000,000 molecular update steps after reaching equilibrium. Whiskered bars represent the standard errors of the replicate runs. Other parameters (if not stated otherwise):
, i.e. left hand side of the light blue curve). The results are averaged over 5 replicate model runs, and over 1,000,000 molecular update steps after reaching equilibrium. Whiskered bars represent the standard errors of the replicate runs. Other parameters (if not stated otherwise): 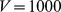 ,
, 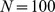 ,
, 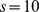 ,
, 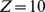 ,
, 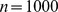 ,
, 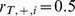 ,
, 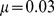 ,
, 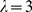 ,
, 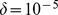 ,
, 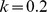 ,
, 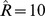 ,
, 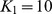 and
and 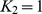 .
.
