Figure 6. Characteristics of secondary structures of complementary strands.
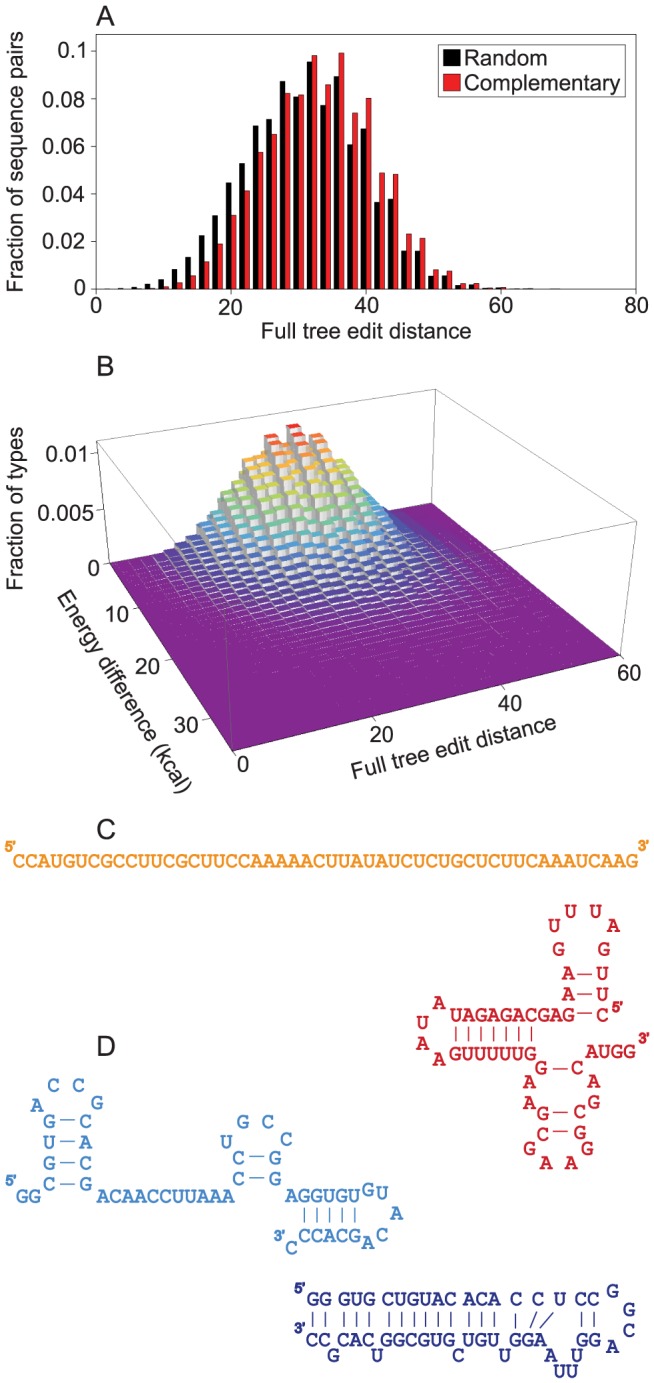
The characteristics of minimum free energy secondary structures are measured on a sample of 107 randomly generated sequences of length 50. In case of complementary strands, the complementary sequences of the randomly generated strands are also analyzed. (A) Complementary strands have higher full tree edit distance between them (red bars) than random sequence pairs (black bars). (B) Energy difference between members of pairs of complementary, folded strands. Around tree edit distance 30 most complementary, folded structures have negligible energy difference, but a decreasing proportion of pairs show a difference of up to 40 kcal. (C) Example of a complementary pair of strands in which one of the strands does not have a structure, while the other has a rich structure. The difference of their minimum free energies is (6.6 kcal). (D) Example of a complementary pair of strands in which the two strands have very different (tree edit distance 68) but still rich structures. The difference of their minimum free energies is (7.0 kcal).
