Figure 1. LN models and  –
– curves for gain-scaling (GS) and nongain-scaling (NGS) neurons.
curves for gain-scaling (GS) and nongain-scaling (NGS) neurons.
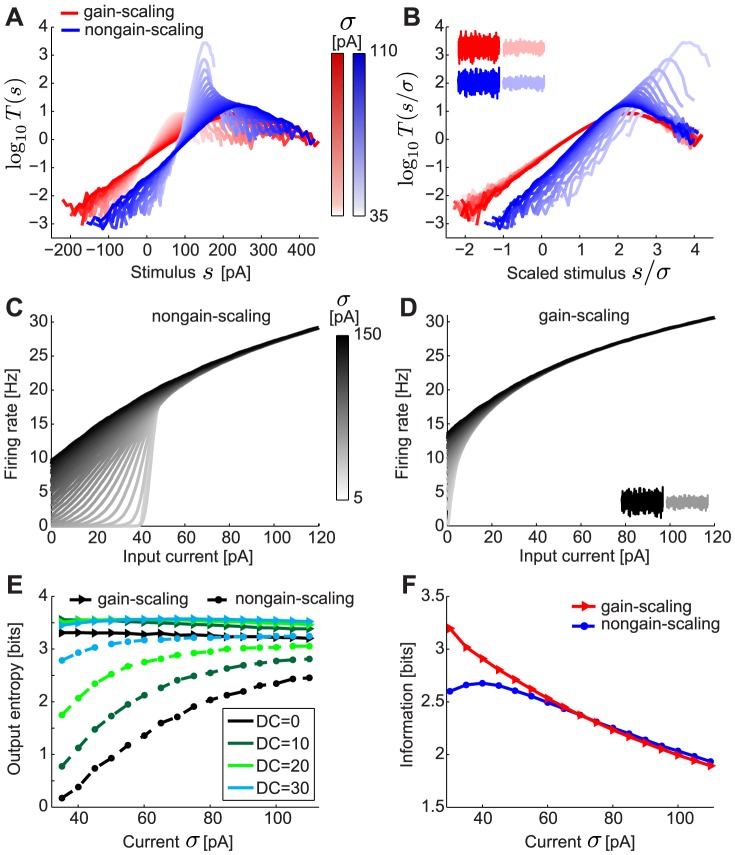
A. The nonlinearities in the LN model framework for a GS (red) ( pS/µm2 and
pS/µm2 and 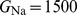 pS/µm2) and a NGS (blue) (
pS/µm2) and a NGS (blue) (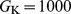 pS/µm2 and
pS/µm2 and 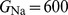 pS/µm2) neuron simulated as conductance-based model neurons (Eq. 2). The nonlinearities were computed using Bayes' rule:
pS/µm2) neuron simulated as conductance-based model neurons (Eq. 2). The nonlinearities were computed using Bayes' rule: 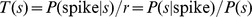 , where
, where  is the neuron's mean firing rate and
is the neuron's mean firing rate and  is the linearly filtered stimulus (see also Eq. 7 in Methods). B. The same nonlinearities as A, in stimulus units scaled by
is the linearly filtered stimulus (see also Eq. 7 in Methods). B. The same nonlinearities as A, in stimulus units scaled by  (magnitude of stimulus fluctuations). The nonlinearities overlap for GS neurons over a wide range of
(magnitude of stimulus fluctuations). The nonlinearities overlap for GS neurons over a wide range of  . C–D. The
. C–D. The 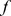 –
–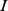 curves for a NGS (C) and a GS neuron (D) for different values of
curves for a NGS (C) and a GS neuron (D) for different values of  . E. The output entropy as a function of the mean (DC) and
. E. The output entropy as a function of the mean (DC) and  (amplitude of fast fluctuations). F. Information about the output firing rate of the neurons as a function of
(amplitude of fast fluctuations). F. Information about the output firing rate of the neurons as a function of  .
.