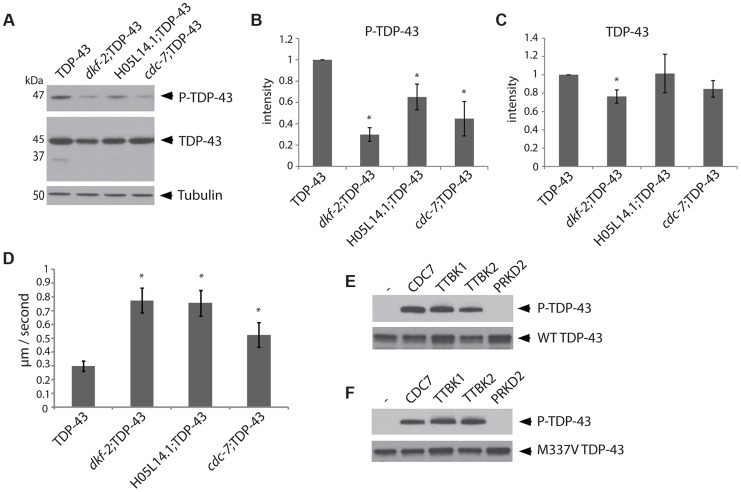
Figure 1. The kinases TTBK1/2 phosphorylate TDP-43 in C. elegans and in vitro.
(A) Developmentally synchronized day 1 adult dkf-2(−/−);TDP-43, cdc-7(−/−);TDP-43, and H05L14.1(−/−);TDP-43 kinase mutants have decreased phosphorylated TDP-43 relative to TDP-43 transgenic animals alone. See S2 Figure for overexposure of immunoblots. Measurement of protein levels of three independent immunoblots is presented for phospho-TDP-43 (B) and total TDP-43 (C). Signal is normalized to the parental TDP-43 transgenic control strain, and graphs are plotted in arbitrary units of intensity. * P<0.05, Student's t-test relative to TDP-43 transgenic control. (D) Developmentally staged kinase mutant/TDP-43 transgenic L4 larvae exhibit significantly higher dispersal velocity relative to TDP-43 transgenic animals with intact kinase genes. Animals were measured for the linear distance traveled from a central reference point over time, N>70 for each genotype. *P<0.05 versus TDP-43. Non-transgenic animals disperse at an average velocity of 5.9 µm/second. (E) In vitro kinase assays testing the kinase activity of TTBK1, TTBK2, and PRKD2 against wild-type TDP-43 demonstrate purified TTBK1 and TTBK2 phosphorylate wild-type TDP-43, while PRKD2 does not. Immunoblots are probed with antibodies for phosphorylated (P-TDP-43) and total TDP-43. (F) In vitro kinase assays demonstrate purified TTBK1 and TTBK2 but not PRKD2 phosphorylate M337V mutant TDP-43. See S4 Figure for controls of kinase activity on known protein substrates.