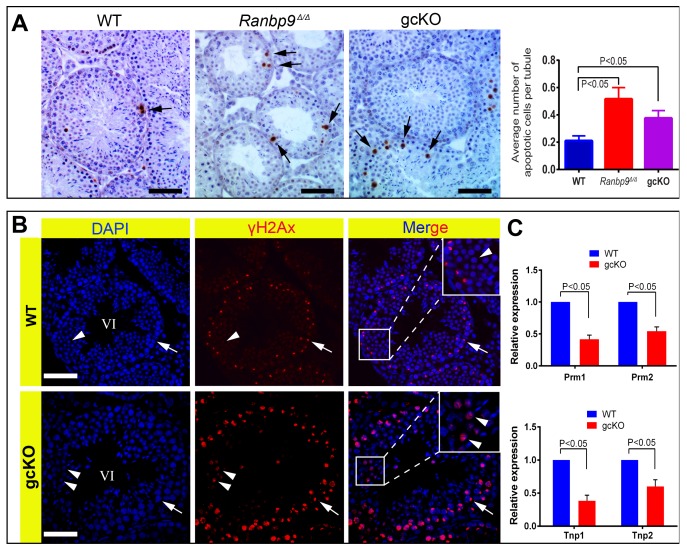
Figure 3. Ranbp9 deficiency causes male germ cell apoptosis and DNA double-strand breaks.
(A) TUNEL assays on WT, Ranbp9 global KO (Ranbp9Δ/Δ) and gcKO testes. Arrows point to apoptotic cells stained in brown. Scale bar = 50 µm. Significantly increased average number of apoptotic cells is observed in both Ranbp9 Δ/Δ and gcKO testis (the far right panel). >60 cross-sections were scored for the average number of apoptotic cells per tubule for each genotype. Three mice of each genotype were analyzed, and data were presented as mean ± SD, n = 3. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of γH2AX in seminiferous tubules of WT and gcKO testes at ∼stage VI. In WT seminiferous tubules, γH2AX immunoreactivity is mostly confined to the XY body (arrows) in pachytene spermatocytes and completely absent in round spermatids (arrowheads). In contrast, in gcKO seminiferous tubules, numerous round spermatids exhibit strong γH2AX staining (arrowheads) in addition to its normal localization in the XY body (arrow) in pachytene spermatocytes. (C) qPCR analyses showing significantly reduced levels of Prm1, Prm2, Tnp1 and Tnp2 mRNAs in 6-week old Ranbp9 gcKO testes. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3.