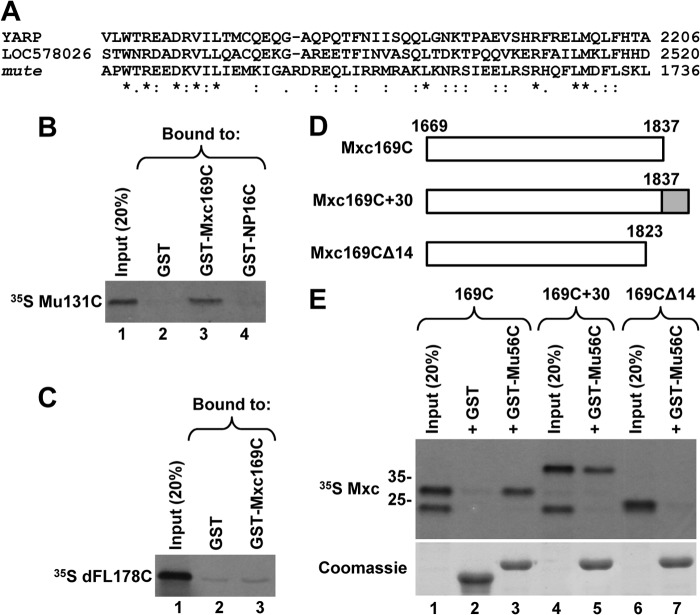
FIGURE 7.
Mute, the Drosophila homologue of YARP, interacts with Mxc. A, Clustal 2.1 multiple sequence alignment of the C-terminal regions of human YARP (2240 amino acids), Strongylocentrotus purpuratus protein LOC578026 (2553 amino acids), and Drosophila melanogaster Mute (1739 amino acids). Identical residues are denoted with an asterisk; conserved (strongly similar properties) and semi-conserved (weakly similar properties) residues are indicated with a colon and a period, respectively. B and C, GST pulldown assay to analyze in vitro interaction of 35S-labeled C-terminal regions of Mute (Mu131C, B) or Drosophila FLASH (dFL178C, C) with the last 169 amino acids of Mxc fused to GST (GST-Mxc169C). GST alone and GST fused to the last 16 amino acids of human NPAT (GST-NP16) were used as negative controls. The amount of each GST protein purified on glutathione beads was monitored by staining the gel with Coomassie Blue (data not shown). D and E, 35S-labeled Mxc169C and its two mutant versions, as depicted in D, were tested for interaction with the last 56 amino acids of Mute fused to GST (GST-Mu56C) (top panel in E). GST was used as a negative control. The amount of each GST protein purified on glutathione beads was monitored by staining the gel with Coomassie Blue (bottom panel in E). Note that inputs for Mxc169C and Mxc169C+30 (lanes 1 and 4) contain an additional 35S-labeled protein migrating below the 25-kDa size marker. This protein is likely generated as a result of premature termination of in vitro translation and it does not interact with GST-Mu56C.