FIGURE 8.
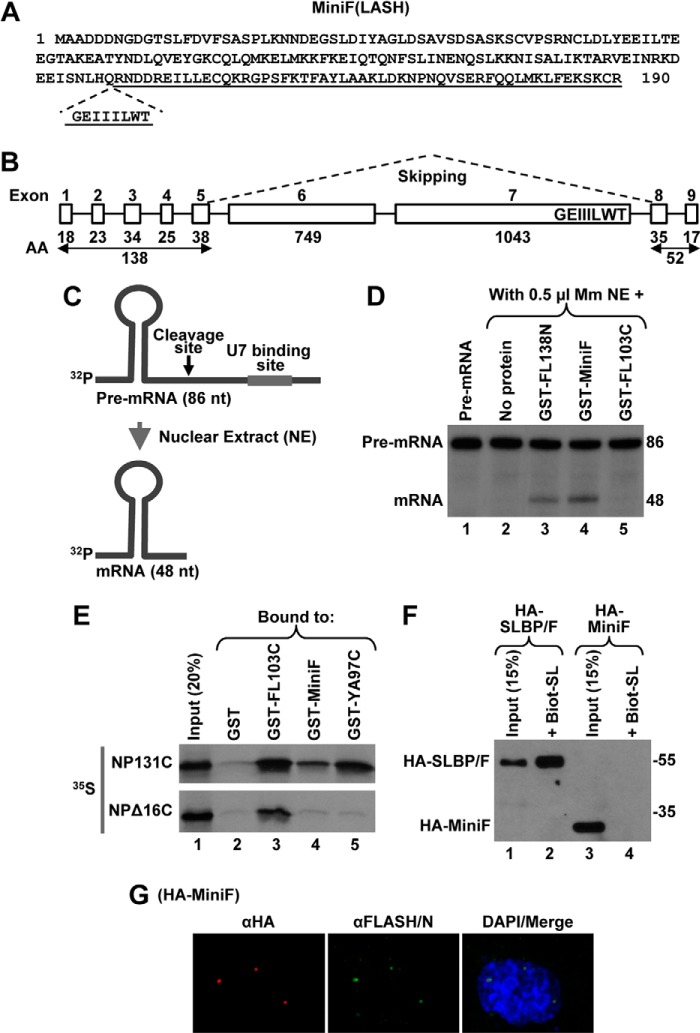
Identification of human MiniFLASH (MiniF). A, amino acid sequence of 190-amino acid human MiniF. The incomplete C-terminal domain is underlined, and the missing GEIIILWT sequence is shown below. B, exon/intron organization of the human FLASH gene. The number of amino acids (AA) encoded by individual exons 1–9 of FLASH are shown at the bottom. The MiniF mRNA results from skipping the two large exons 6 and 7, as depicted by dashed lines, and in-frame linking of the N- and C-terminal exons. The highly conserved GEIIILWT sequence of the C-terminal domain of FLASH that is encoded by the end of exon 7 and hence missing in MiniF is indicated. C, diagram of the histone pre-mRNA substrate (86 nucleotides (nt)) and the product of in vitro 3′ end processing (48 nucleotides) carried out in a nuclear extract (NE). The HDE that is located downstream of the cleavage site (arrow) and serves as binding site for U7 snRNP is indicated with a thick line. D, 3′ end processing of the 86-nucleotide pre-mRNA substrate in 0.5 μl of mouse myeloma (Mm) nuclear extract alone (lane 2) or in the presence of 100 ng of indicated GST fusion FLASH proteins (lanes 3–5). The input substrate is shown in lane 1. E, GST-pulldown assay to analyze the interaction between MiniF and the C-terminal region of NPAT. Bacterially expressed proteins indicated at the top of lanes 2–5 were incubated with 35S-labeled NP131C or NPΔ16C, and the amount of each radioactive protein absorbed on glutathione beads was determined by autoradiography. As determined by Coomassie Blue staining, the amount of GST proteins in each lane was comparable (data not shown). Lane 1 contains 20% of each radioactive protein used in the experiment. F, transient expression of HA-MiniF in HeLa cells was compared with expression of HA-SLBP/F (lanes 3 and 1, respectively). As expected, only HA-SLBP/F can be purified by binding to the Biot-SL (lane 2). G, immunofluorescence of HeLa cells transiently expressing HA-MiniF. HA-MiniF was detected by a mouse anti-HA antibody and stained red. HLBs were detected by an antibody against the N-terminal FLASH and stained green. Nuclei were visualized by staining with DAPI.