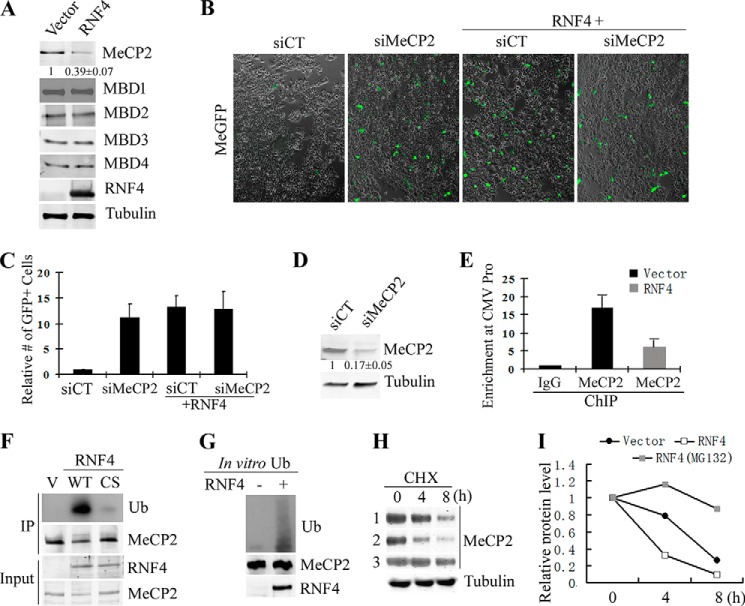
FIGURE 3.
RNF4 ubiquitinates and turns over MeCP2. A, Western blot analysis indicates that the level of MeCP2, but not other MBD proteins, is reduced by co-expression of RNF4. Values represent the mean of three independent experiments ± S.D. B and C, representative images (B) and quantification (C) of the expression of MeGFP reporter in scrambled siRNA control and MeCP2 knockdown cells. GFP expression is derepressed by MeCP2 knockdown and is not further activated by RNF4. The number of GFP-positive cells per field was quantified, and the value of control was set as 1. Results from three independent experiments ± S.D. are shown. siCT, scrambled siRNA control. D, Western blot confirms the knockdown of MeCP2. Values represent the mean of three independent experiments ± S.D. E, ChIP-qPCR reveals that MeCP2 binds to the promoter of the methylated GFP reporter, and MeCP2 binding is significantly reduced by RNF4 expression. Results from three independent experiments ± S.D. are shown. F, RNF4 ubiquitinates MeCP2. MeCP2 was immunoprecipitated (IP) from cells expressing RNF4 WT or CS mutant, and ubiquitination (Ub) level was analyzed by Western blotting. RNF4 WT, but not the CS mutant, significantly promotes MeCP2 ubiquitination. V means empty vector control. G, RNF4 directly ubiquitinates MeCP2. Purified RNF4 and MeCP2 proteins were subjected to in vitro ubiquitination assay. H, Western blot of MeCP2 levels in vector control (lane 1) and RNF4 (lanes 2 and 3) transfected cells. Cells were treated with cycloheximide (CHX) and collected for analysis at different time points. Samples of lane 3 were co-treated with MG132 to block proteasome activity. I, densitometry quantification for panel H shows that RNF4 significantly accelerates the turnover of MeCP2, which is blocked by inhibition of proteasome.