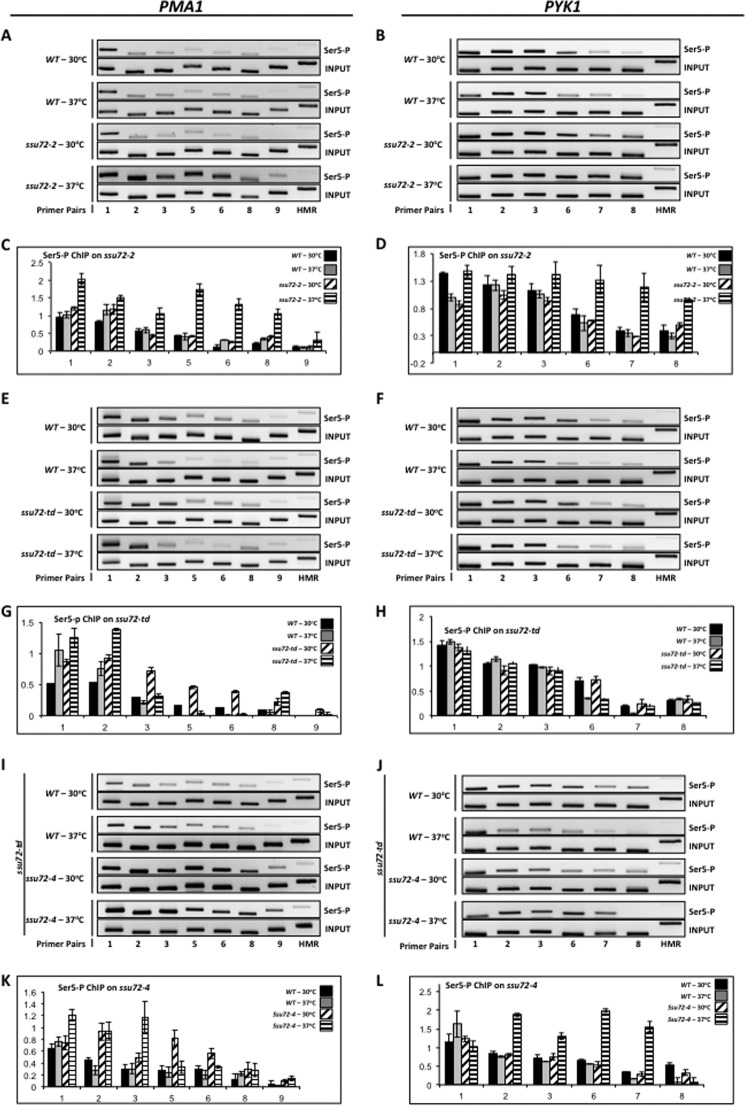
FIGURE 2.
Loss of Ssu72 phosphatase activity results in accumulation of the Ser(P)5 form of RNAPII across the PMA1 and PYK1 genes. A, ChIP analysis of Ser(P)5 cross-linking to PMA1 using isogenic strains H-51 (WT) and YMH650 (ssu72-2). Chromatin was immunoprecipitated using monoclonal antibody 3E8 (α-Ser(P)5). B, ChIP analysis of Ser(P)5 cross-linking to PYK1 using the same strains and conditions as in A. C, quantification of the data shown in A. D, quantification of the data shown in B. E, identical to A, except chromatin was immunoprecipitated from isogenic strains FY23 (WT) and XH-24 (ssu72-td). F, identical to B, except chromatin was immunoprecipitated from isogenic strains FY23 (WT) and XH-24 (ssu72-td). G, quantification of the data shown in E. H, quantification of the data shown in F. I, ChIP analysis of Ser(P)5 cross-linking to PMA1 using the XH-24 strain transformed with plasmid DNA carrying either wild type SSU72 (pM712, labeled as WT), or catalytically inactive ssu72-C15S (pM698, labeled as ssu72-4) (Table 1). Strains were incubated at either the permissive (30 °C) or restrictive (37 °C) temperature for 1 h prior to cross-linking. J, ChIP analysis of Ser(P)5 cross-linked to PYK1 using the same strains and conditions as in I. K, quantification of the data shown in I. L, quantification of the data shown in J.