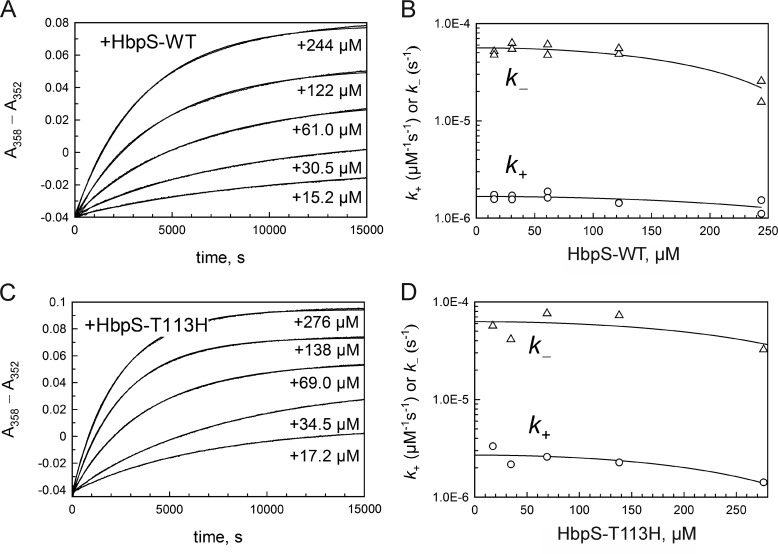
FIGURE 6.
Kinetics of interaction between HbpS (wild type and mutant T113H) and H2OCbl+. A, binding reaction of HbpS-WT. The reactants H2OCbl+ (a0 = 19.0 μm) and HbpS (monomer concentrations of b0 = 15 - 244 μm) were mixed, and absorbance changes (A358 − A352) were traced over time. Curves were approximated by Equation 2 to calculate k+ and k− (ϵ = 0.00658 μm−1cm−1). B, rate constants versus protein concentration. The values of k+ and k− from panel A (and the data of a parallel experiment, not shown) were plotted versus the concentration of HbpS-WT (monomers). The charts were approximated by the empirical functions k+ = 1.67·10−6 − 6.32·10−12x2 and k− = 5.62·10−5 − 5.78·10−10x2. The first parameter of each function predicts the rate constant at a low protein concentration: k+ = 1.67 ± 0.14 m−1s−1, and k− = (5.62 ± 0.52)·10−5 s−1. C, binding reaction of HbpS-T113H. The reactants H2OCbl+ (a0 = 19.0 μm) and HbpS (b0 = 17 - 276 μm) were mixed. and the time course of absorbance (A358 − A352) was recorded. Curves were approximated by Equation 2 to calculate k+ and k− (ϵ = 0.00779 μm−1cm−1). D, rate constants versus protein concentration. The values of k+ and k− from panel C were plotted versus the concentration of HbpS-T113H mutant (monomers). The charts were approximated by the empirical functions k+ = 2.77·10−6 − 1.72·10−11x2 and k− = 6.27·10−5 − 3.34·10−10x2. The first parameter of each function predicts the rate constant at a low protein concentration: k+ = 2.77 ± 0.61 m−1s−1, and k− = (6.27 ± 0.23)·10−5 s−1.