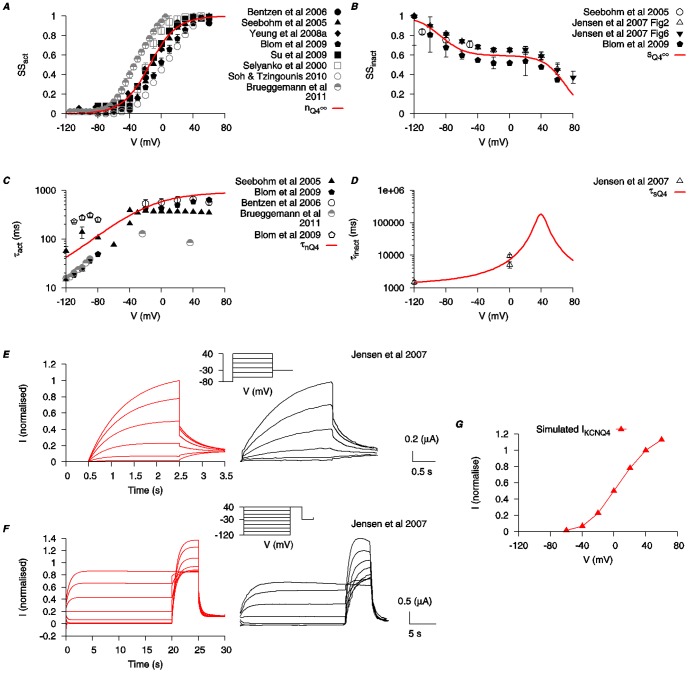
Figure 4. Biophysical characteristics of KCNQ4 current.
Properties of I KCNQ4 are developed using experimental data from mammalian KCNQ4 clones expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes (black) and other expression systems (gray) [25], [30]–[32], [34], [36]–[39]. A, V-dependent activation steady state (n Q4∞). B, V-dependent inactivation steady state (s Q4∞). C, V-dependent activation time constant (τn Q4). D, V-dependent inactivation time constant (τs Q4). E and F, simulated time tracings of I KCNQ4 with two different voltage-clamp protocols from Jensen et al. (2007) [32] (insets) and the experimental time tracings are shown for comparison. (Experimental tracing adapted with permission from Jensen et al. (2007); copyright 2007, Biophysical Society.) G, simulated I-V relationship of I KCNQ4 using the same voltage-clamp protocol as in E. All I-V data are normalized to the maximal current value at V = 40 mV.