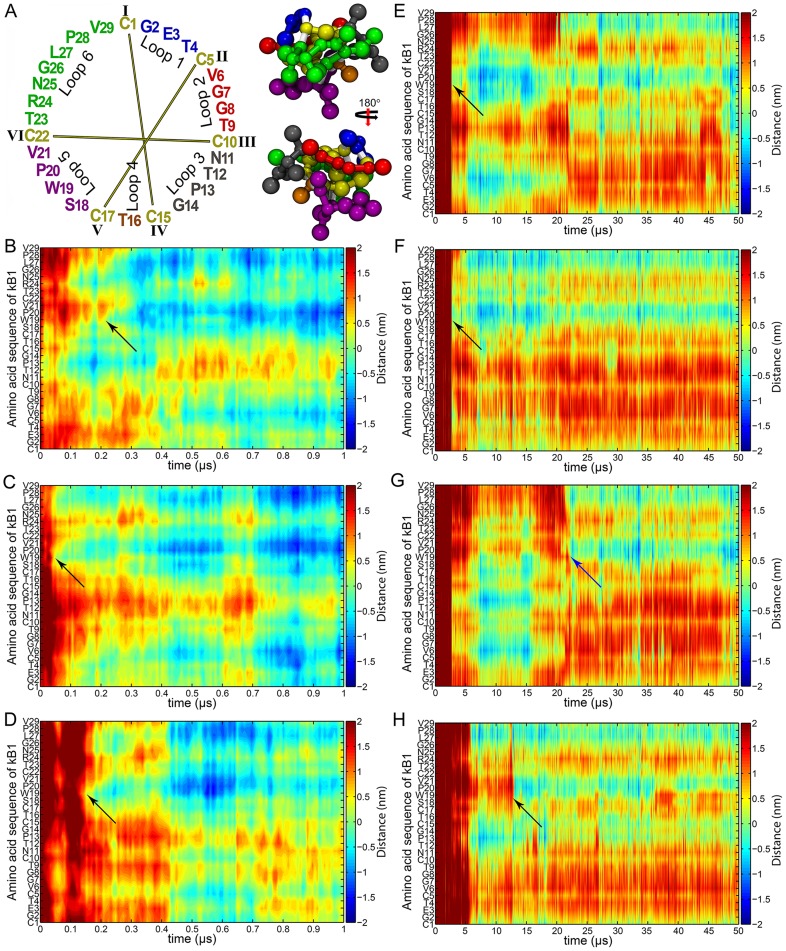
Figure 1. Membrane binding progression of kB1.
(A) Sequence and coarse-grained model of kB1 structure. The amino acid (AA) sequences of kB1 and other cyclotides are divided into six loops. Loops 1–6 of kB1 are colored blue, red, grey, orange, violet and green, respectively. Cysteine is shown in yellow and disulfide bonds are presented with yellow lines. The structure of kB1 is shown as a space-filling CPK model. The loop colors are the same as those shown for the sequence. The peptide bond of any AA residue to cysteine is shown in white. The distances of all AA residues relative to the membrane surface of the monomer in the (B) M1, (C) M2 and (D) M3 simulations are presented. The relative distances are shown during 0–1 µs to clearly demonstrate the activity of Trp19 in the membrane binding process of kB1. The distances of all AA residues of kB1 molecules (E) A, (F) B, (G) C and (H) D in the tetramer relative to the membrane surface during the entire simulations are shown. Black arrows show the membrane binding of Trp19. The blue arrow shows the binding of the Trp19 of molecule C to the membrane at approximately 22.3 µs, which was the time that the tetramer completed its membrane binding process.