Fig. 2.
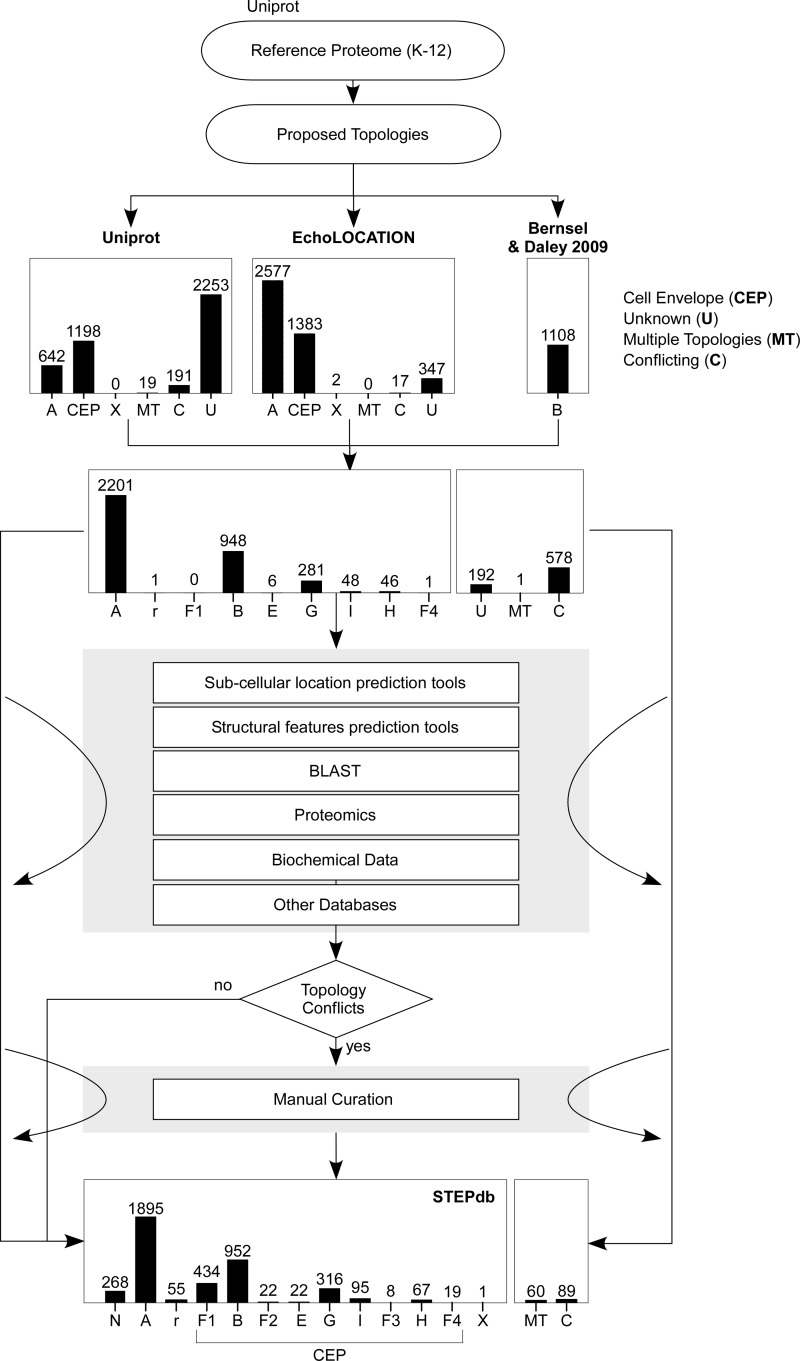
Annotation of subcellular topologies of the E. coli K-12 proteome. The E. coli K-12 reference proteome was downloaded from Uniprot (July 2014; (29)). Respective subcellular annotation from Uniprot (29) was retrieved for 2050 proteins (∼46% of the total proteome; Table I). Subcellular annotation was also downloaded from EchoLOCATION (32) that lists 4345 proteins that were matched to 3957 proteins of the E. coli reference proteome (Table I). The annotation of IM proteins we based on a proteomic analysis that contributed 1108 IM proteins (33). The subcellular terminologies of the two databases were assigned to a STEPdb subcellular class (supplemental Table S4). Amalgamation of these three resources contributed a total of 4111 proteins with an already existing proposed annotation in at least one resource leaving 195 proteins of unassigned topologies and 576 proteins with contradicting proposed subcellular location (Table I). To determine the a subcellular location for the unknown proteins and to resolve the annotation differences we sought to utilize bioinformatics tools that can predict subcellular location or other structural motifs and sequence alignment (supplemental Fig. S2). The core tools utilized were: SignalP, TatP, LipoP, Phobius (8, 9, 12, 13) used for the prediction of secretion motifs, PSORT-B (11) for the prediction of subcellular location and TMHMM, Phobius (9, 36) for the prediction of transmembrane helices. A set of additional bioinformatics tools (Prediction Tools 2) comprising Protscale for hydrophobicity (116), SOSUI, ClubSub, LocTree3 for subcellular location (10, 37, 38) AmphipaSeek for amphipathic in-plane membrane anchors (51) and BLAST (117) was employed to locate additional autotransporters. The comparison between the existing annotations and the predictions of the bioinformatics tools lead to more conflicts regarding the proposed subcellular topologies (supplemental Table S8). To resolve these annotation differences we sought experimental evidence in proteomic, genomic and biochemical studies (supplemental Table S7A).