Figure 2.
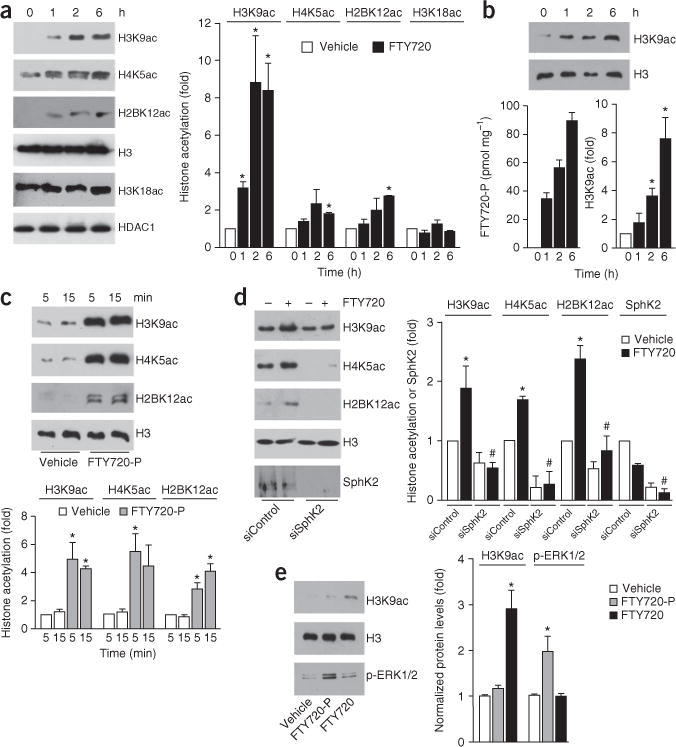
FTY720-P enhances specific histone acetylations. (a,b) SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells (a) or primary hippocampal neurons (b) were treated with FTY720 (5 μM) for the indicated times (N = 3 independent cell culture replicates per group). Histone acetylations in nuclear extracts were detected by immunoblotting with antibodies to specific histone acetylation sites and nuclear levels of FTY720-P were determined by LC-ESI-MS/MS (b). (c) Purified nuclei from naive SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells were incubated for the indicated times with vehicle or FTY720-P (1 μM) and histone acetylations determined. *P < 0.01 as compared to vehicle; unpaired Student’s t-test. (d) Purified nuclei were isolated from neuroblastoma cells transfected with siControl or siSphK2 and incubated with vehicle or FTY720 (1 μM) for 15 min. Histone acetylations were determined by immunoblotting. (e) Naive neuroblastoma cells were treated with vehicle, FTY720-P (100 nM) or FTY720 (1 μM) for 2 h and nuclear extracts analyzed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. Quantified data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05 as compared to vehicle and #P < 0.01 as compared to siControl treated with FTY720 (unpaired Student’s t-test). H3 was used as an internal loading control. (a–e) *P < 0.05 as compared to vehicle (unpaired Student’s t-test). (d) #P < 0.01 as compared to siControl treated with FTY720 (unpaired Student’s t-test). All western blots were performed three times. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 10.
