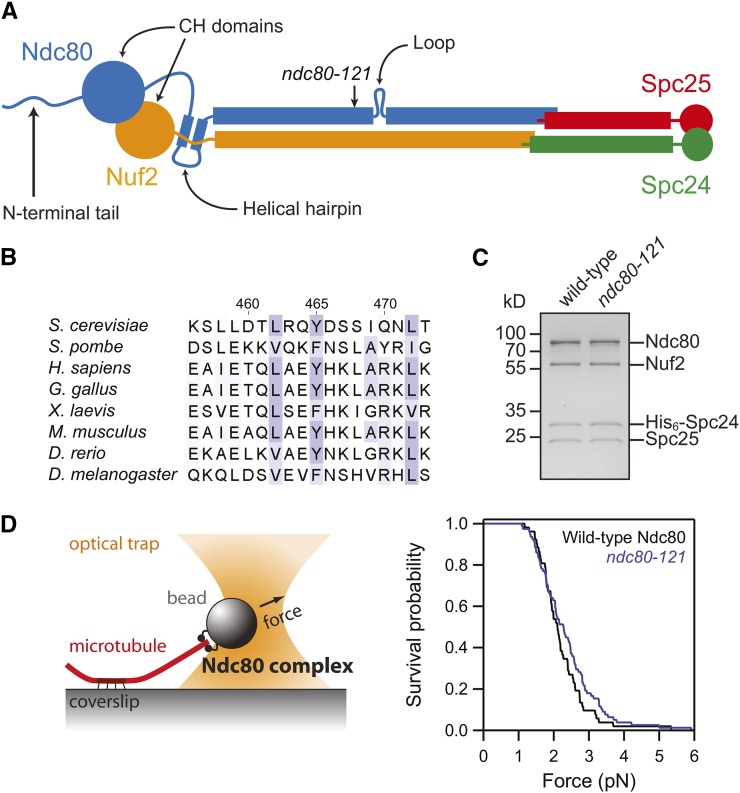
Figure 1.
The ndc80-121 mutations affect conserved residues in Ndc80 and do not disrupt assembly of an intact Ndc80 complex. (A) Schematic of the Ndc80 complex, with the site of the ndc80-121 mutations noted. (B) Sequence alignment of the region of Ndc80 mutated in the ndc80-121 allele (Y465C I469Q). Alignments were performed with ClustalW2 (Larkin et al. 2007) and residues are colored based on Blosum62 scores in Jalview (Waterhouse et al. 2009). (C) Coomassie-stained gel of recombinant Ndc80 complex containing the ndc80-121 mutations. The mutant complex migrated similarly to the wild-type complex by gel filtration and was collected at the same elution volume. (D) Left: schematic of rupture force assay. Right: survival vs. force curves for beads coated with wild-type (black trace, n = 52) or mutant (blue trace, n = 78) Ndc80 complexes. The two distributions are not significantly different, as determined by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test (P = 0.4).