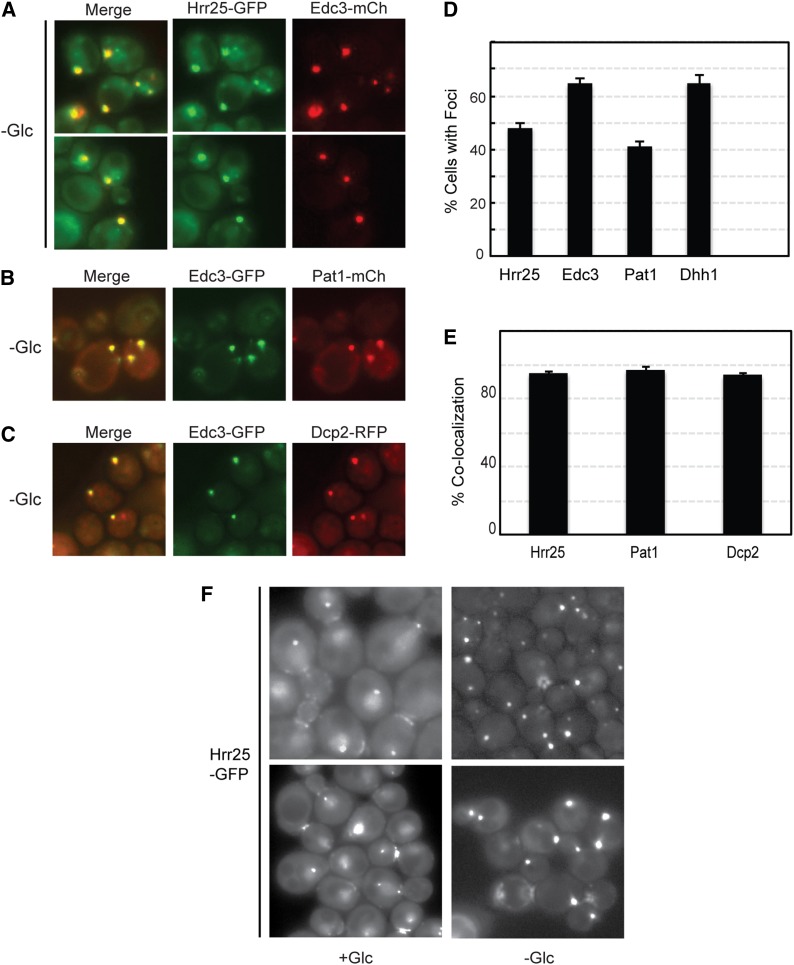
Figure 11.
Hrr25 was efficiently recruited to P-body foci after a brief period of glucose starvation. (A) Yeast cells expressing the Hrr25-GFP fusion protein were grown to log phase and then transferred for 15 min to a medium that lacked glucose. Two representative images of the colocalization observed between Hrr25 and the Edc3-mCh reporter are shown. (B and C) Fluorescence microscopy images showing the colocalization observed between Edc3-GFP and either Pat1-mCh (B) or Dcp2-RFP (C) after a 15-min starvation for glucose. (D) Hrr25 formed cytoplasmic foci at a frequency similar to that observed for known P-body reporters. The foci were induced by a 15-min starvation for glucose as described in A. The graph values represent the quantitation of the microscopy data shown in A–C and are the average of at least two independent experiments (n = 100). (E) Hrr25 displayed a high level of colocalization with the P-body reporter Edc3. Quantitation of the colocalization data presented in A–C; the bars represent the degree of colocalization observed between Edc3 and the indicated proteins. (F) The intracellular localization of Hrr25 was altered by an acute starvation for glucose. Cells expressing a Hrr25-GFP fusion protein were examined by fluorescence microscopy before (+Glc) and after a 15-min starvation for glucose (−Glc). Two representative images are shown for each.