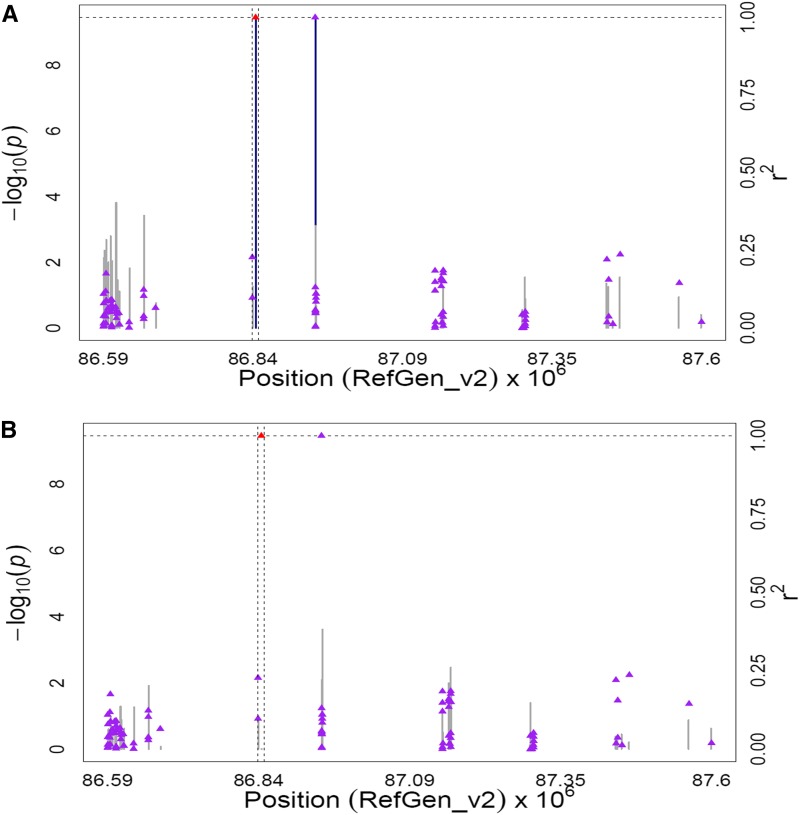
Figure 3.
GWAS for the ratio of α-carotene to zeinoxanthin content in maize grain. (A) Scatter plot of association results from a unified mixed model analysis of the ratio of α-carotene to zeinoxanthin and LD estimates (r2) across the lut1 chromosome region. Negative log10-transformed P-values (left y-axis) from a GWAS for the ratio of α-carotene to zeinoxanthin and r2 values (right y-axis) are plotted against physical position (B73 RefGen_v2) for a 1-Mb region on chromosome 1 that encompasses lut1. The blue vertical lines are –log10 P-values for SNPs that are statistically significant for the ratio of α-carotene to zeinoxanthin at 5% FDR, while the gray vertical lines are –log10 P-values for SNPs that are nonsignificant at 5% FDR. Triangles are the r2 values of each SNP relative to the peak SNP (indicated in red) at 86,844,203 bp. The black horizontal dashed line indicates the –log10 P-value of the least statistically significant SNP at 5% FDR. The black vertical dashed lines indicate the start and stop positions of lut1 (GRMZM2G14322.) (B) Scatter plot of association results from a conditional unified mixed model analysis of the ratio of α-carotene to zeinoxanthin and LD estimates (r2) across the lut1 chromosome region, as in A. The peak SNP from the unconditional GWAS (ss196425306; 86,844,203 bp) was included as a covariate in the unified mixed model to control for the lut1 effect.