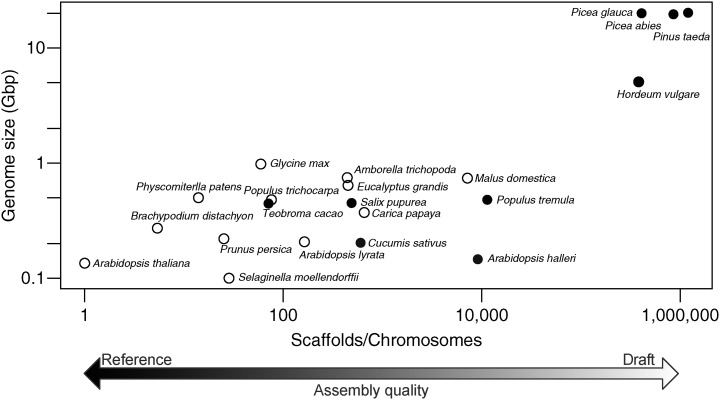
Figure 1.
Size and assembly of conifer genomes compared with other plant genomes. Genome size is plotted against the number of scaffolds divided by the haploid chromosome number for a range of plant species. As such, an assembly that reconstructs a genome with perfect contiguity will have a value of 1, and values greater than 1 represent increasing genome fragmentation. Genome assemblies that utilized Sanger sequencing either in full or in part are represented as white circles. Assemblies constructed using only next generation sequencing technologies are represented as black circles. Both axes are plotted on a log10 scale. With the exception of Populus tremula, Hordeum vulgare, and the three conifer genomes, all genomes were obtained from the Phytozome resource (version 10; http://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/). The early release draft assembly of P. tremula was obtained from the PopGenIE.org FTP resource (ftp://popgenie.org/popgenie/UPSC_genomes/UPSC_Draft_Assemblies/Current/Genome/) and H. vulgare ‘Morex’ from the Munich Information Center for Protein Sequences barley genome database FTP resource (ftp://ftpmips.helmholtz-muenchen.de/plants/barley/public_data/sequences/). The conifer genomes are detailed by Birol et al. (2013), Nystedt et al. (2013), and Zimin et al. (2014).