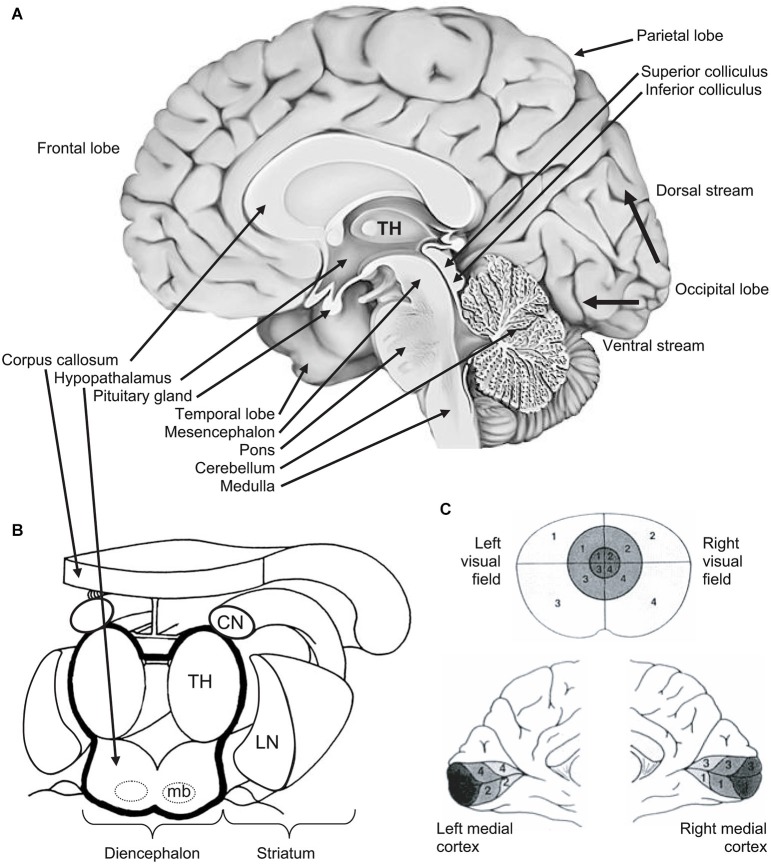
Figure 2.
(A) Medial view of right hemisphere showing the brainstem and its three levels (from bottom to top: medulla, pons, mesencephalon), the diencephalon, the telencephalon and its four hemispheric lobes (clockwise: frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal). From the primary visual area (V1) in the occipital cortex, thin black arrows show the ventral (down) stream and the dorsal (up) streams. (B) 3D view of diencephalon and striatum. The diencephalon is delineated by a thick black line. The striatum (CN: caudate nucleus; LN: lentiform nucleus) is in close vicinity of the diencephalon. (C) Retinotopy of the retino-occipital visual pathway: organization of projections of the visual field (upper part) in the occipital cortex where the primary visual cortex (or V1) is spread around the calcarine sulcus (medial views in the lower part). Information from central visual field (foveal vision—the darkest in the figure) is projected and over-represented in the posterior part of occipital cortex. Other notations: mb: mammillary bodies; TH: thalamus. From O.A. Coubard (© O.A. Coubard, with permission).