Figure 4.
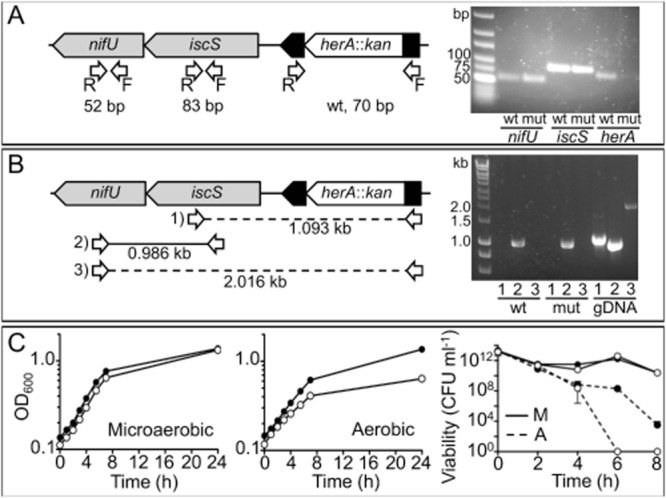
A. Left: Mutagenesis strategy of herA, the arrangement of its surrounding gene region and screening for polar effects on expression. A herA::kan mutant was created by deletion and insertion of a kanamycin resistance cassette to replace most of the coding region of cj0241c. herA itself is positioned downstream of cj0243c (not pictured) and upstream of iscS and nifU. Arrows indicate RT-PCR primer annealing sites, with expected product sizes shown underneath (bp = base pairs). Right: 3% agarose gel showing results of RT-PCR using cDNA produced from mRNA extracted from wild-type (wt) and herA::kan (mut) strains, and primer pairs for each gene. B. Left: Further RT-PCR using a combination of primer pairs (numbered). Full lines indicate successful reaction, broken lines indicate unsuccessful. Expected product sizes following RT-PCR are shown underneath each reaction (kb = kilobase pairs). Right: 1% agarose gel showing these reactions with cDNA produced from mRNA extracted from wild-type (wt) and herA::kan mutant (mut) strains, compared with wild-type genomic DNA as template (gDNA). C. Microaerobic (left panel) and aerobic (middle panel) growth of wild-type (closed circles) and herA::kan (open circles). For aerobic conditions in this experiment, 50 ml cultures in 250 ml un-baffled conical flasks were shaken at 180 r.p.m. in air (these conditions allowed initial growth of both wild-type and mutant). Right panel: Viability of wild-type (closed circles) and herA::kan (open circles) during microaerobic incubation (solid line) and aerobic (dashed line) incubation.
