Figure 1.
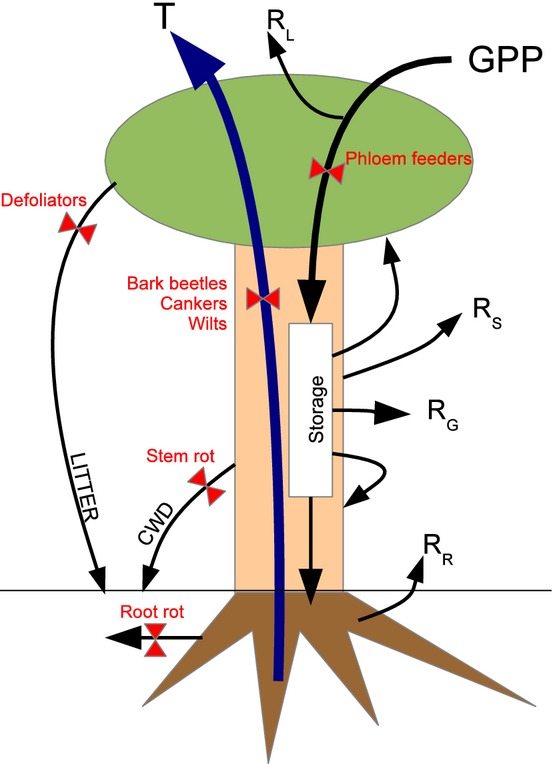
A general model for incorporating biotic disturbance in ecosystem models. A typical ecosystem model predicts GPP based on enzyme kinetics or light-use efficiency and is closely coupled to transpiration through stomatal regulation. Plants then allocate stored carbon to leaf, root and stem pools minus construction costs (growth respiration, Rg). Maintenance respiration (Rl, Rs and Rr) and turnover then deplete each of these pools to CO2 and soil organic matter respectively. Biotic disturbances (red font) act by altering one or more of these flux terms (red valves): For leaves and roots this is through a percent (%) acceleration of turnover rates; for sapwood a % hydraulic reduction; for heartwood a % loss of physical strength and for storage a % loss of inputs.
