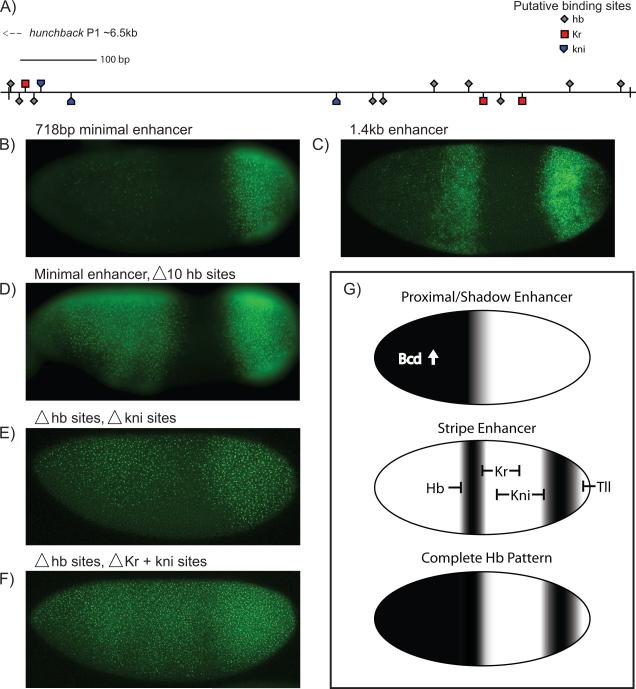
Fig. 4. Analysis of the Hb stripe enhancer.
Transgenic embryos expressing different versions of the Hb stripe enhancer were attached to a yellow reporter gene. The 1.4 kb stripe enhancer contains >30 potential Hb sites, at least 8 potential Kr sites, and 6 potential kni sites, and produces strong stripes of expression in central and posterior regions (C). A minimal, 718 bp stripe enhancer produces a weak central stripe and strong posterior stripe (B), putative binding site locations shown in (A). There is augmented expression and an anterior expansion of the anterior stripe>yellow staining pattern upon site-specific mutations in 10 Hb binding sites (D). There is a further expansion of the staining pattern upon mutagenesis of 3 putative kni sites (E) and even more dramatic expansion upon mutagenesis of the 3 putative Kr and 3 putative Kni sites (F); see Fig S2 for details on enhancer structure and specific binding sites. A proposed model is shown in (G). The complete Hb pattern is a composite of three enhancer inputs; the proximal and shadow enhancers rely on activation by anterior Bcd, while the stripe enhancer is instead ubiquitously activated and carved out by gap repressors. The composite boundary is both steeper and shifted posteriorly with the addition of the stripe enhancer's input.