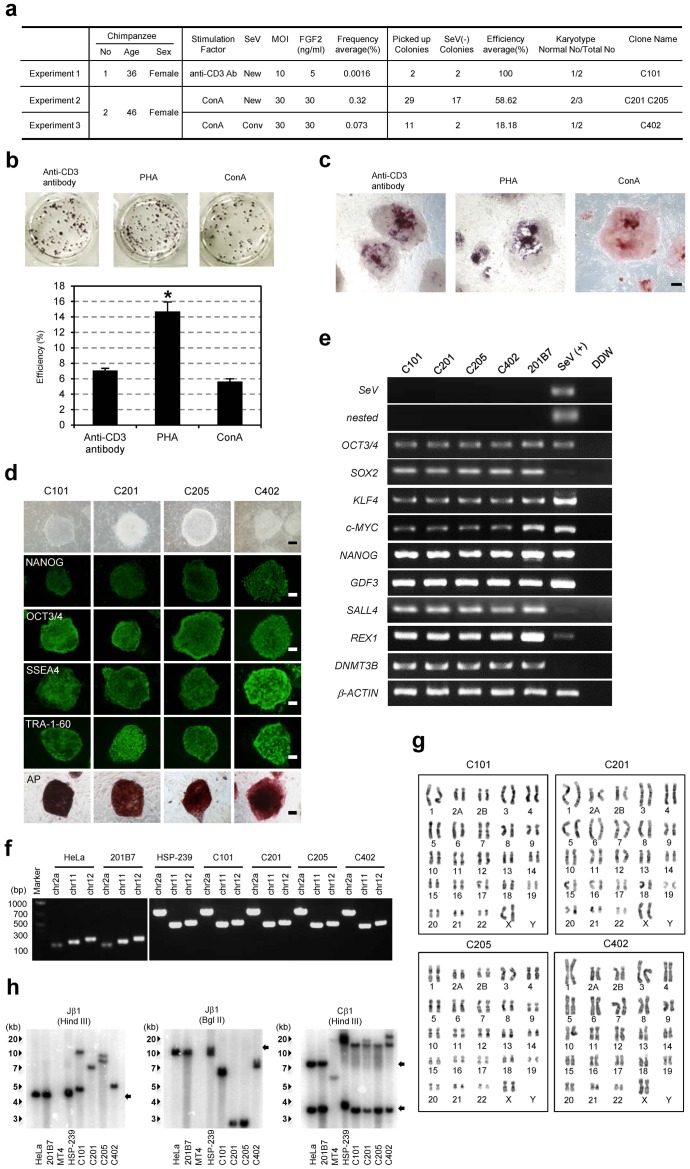
Figure 3. Generation of chimpanzee iPSCs with the TS12KOS vector.
(a) Summary of chimpanzee iPSC generation. iPSCs were generated from the blood cells of two chimpanzee individuals with TS12KOS or the conventional SeV vectors. (b) Effect of the T lymphocyte stimulation on iPSC generation. Experiments were conducted in triplicate (mean ± SD). *P<0.01, PHA versus anti-CD3 antibody or Con A stimulations, Student's t-test. (c) Colony morphology and AP staining of iPSCs from stimulated T lymphocytes. (d) Phase contrast images, immunofluorescence for pluripotency markers, and alkaline phosphatase (AP) staining of chimpanzee iPSC lines. C101, C201, C205, and C402 are described in Fig. 3a. Scale bars, 200 µm. (e) RT-PCR analysis of SeV and human ES cell markers. SeV, first RT-PCR for SeV; nested, nested RT-PCR for SeV; 201B7, control human iPSC line; SeV(+), Day 7 SeV-infected human fibroblasts. (f) PCR products with primers that can distinguish chimpanzee and human genomes. Chimpanzee PCR products; 782, 472 and 504 bps, Human PCR products; 203, 245, 278 bps. (g) Chromosomal analyses of chimpanzee iPSC lines generated with the TS12KOS vector. (h) TCR gene recombination. Genes from the chimpanzee iPSC lines were digested with the indicated enzymes and hybridized with the TCR probes by Southern blotting. Arrows indicate the germ bands of TCR genes. HeLa and 201B7: human cell lines, MT4: human T cell line, HSP-239: chimpanzee T cell line.