Figure 1.
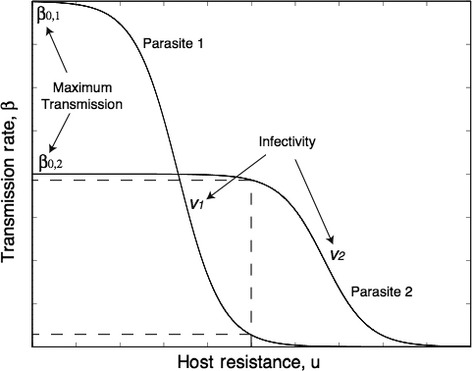
Illustration of the infection function used in the theoretical model in equation (2). Parasite 1 has a small infection range (v1) but achieves high transmission rates against those hosts it can infect. In contrast, parasite 2 has a large infection range (v2) but infects these hosts at a lower rate. Hosts with low resistance ranges (u) will be infected by more parasite types but are assumed to have higher birth rates.
