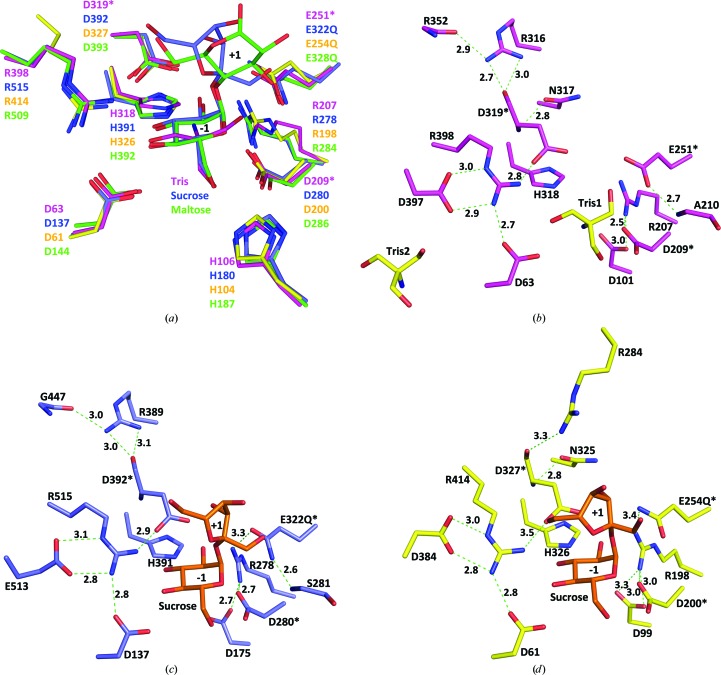
Figure 4.
The similar active-site architecture. (a) Superposition of the −1 subsites of DrTS-N253A–Tris (megenta), XaSH-E322Q–sucrose (slate), NpAS-E328Q–maltoheptaose (green) and RhSI-E254Q–sucrose (yellow). The residue numbering is labelled in the same colour for each protein. The conserved active-site residues of DrTS occupy similar spatial positions to those of XaSH, NpAS and RhSI. Interestingly, the nonreducing terminal maltosyl residue in the NpAS–maltoheptaose complex fits the −1 and +1 subsites of DrTS well. (b)–(d) The interaction networks between the catalytic triad and the surrounding residues in DrTS-N253A–Tris (b), XaSH-E322Q–sucrose (c) and RhSI-E254Q–sucrose (d). The triad residues are indicated by an asterisk.