Figure 2.
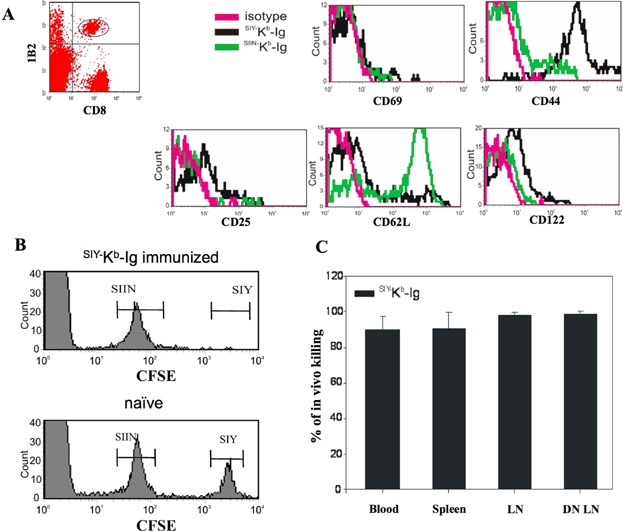
Phenotypic and functional characterization of adoptively transferred 2C T cells after pep−MHC-Ig immunization. (A) 3 × 106 purified 2C T cells were adoptively transferred into C57BL/6 mice. On day 2 after transfer, the recipient mice were treated with 10 µg/mouse anti-CD40 mAb and on day 3 immunized with SIY− Kb-Ig or SIIN−Kb-Ig s.c. Peripheral blood was taken from the recipient mice at day 5 after immunization and stained with anti-CD8 and anti-2C TCR clonotypic mAb (clone 1B2) in combination with either anti-CD25, anti-CD44, anti-CD62L, anti-CD69, anti-CD122, or with the appropriate antibody isotype control. For analysis whole PBMC were first gated on 1B2+/CD8+ and further analyzed for activation marker expression. (B) In vivo CTL killing assay for adoptively transferred 2C T cells. Five days after immunization with SIY−Kb-Ig (upper panel) or naïve animals (lower panel) were injected with 1 × 107 syngeneic splenocytes consisting of both an SIY peptide-pulsed, 2.5 µM CFSE labeled population and an SIIN peptide-pulsed, 0.25 µM CFSE labeled population (1:1 ratio). Eighteen hours later, peripheral blood was taken and analyzed for CFSE labeled cells by flow cytometer. One representative mouse each was displayed. (C) Cumulative in vivo killing data after SIY−Kb-Ig immunization separated by organ. Data have been calculated as % of in vivo killing = 100 − ([(% specific peptide pulsed cells in immunized B6/% unspecific peptide pulsed cells in immunized B6)/(% peptide pulsed in naïve B6/% unspecific peptide pulsed cells in naïve B6)] × 100) and presented as (average ± SD).
