Figure 1.
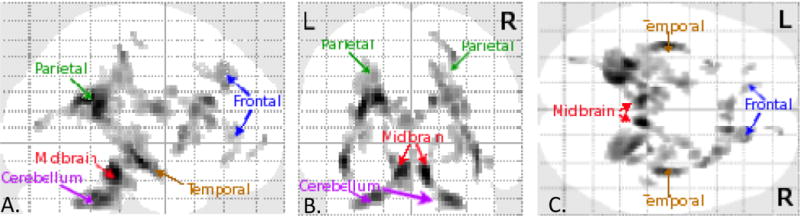
Orthogonal collapsed sagittal (A.), coronal (B.), and axial (C.) views of brain map for significant differences in FA for subjects with d-TGA versus controlss. Areas in which subjects with d-TGA white matter FA is significantly lower than that of control subjects is given by gray scale shading and is located in deep white matter of both hemispheres in frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes as well as cerebellum and midbrain. L=left; R=right.
