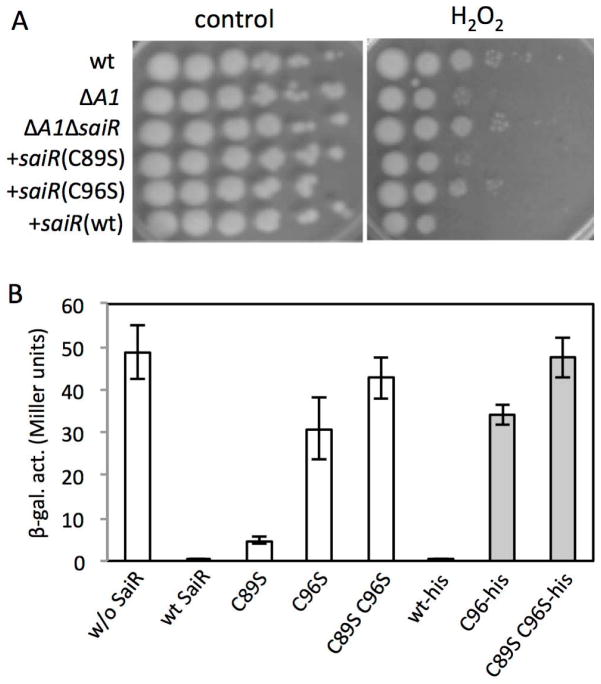
Fig. 3. Cys96 in SaiR is required for repressor activity.
A. H2O2 sensitivity assays were carried out as previously described. Five μl of 10-fold serial dilutions of cells (left to right) were spotted onto LB agar with and without 0.44 mM H2O2. The saiR genes, which encode the wild-type, C89S, and C96S protein, were introduced into the ICEBs1 element of the ΔspxA1ΔsaiR mutant. Strains: wt (7702SR1); ΔspxA1 (ORB8398); ΔspxA1ΔsaiR (ORB8611); ΔspxA1ΔsaiR +saiR(wt) (ORB8725); ΔspxA1ΔsaiR +saiR(C89S) (ORB8723); ΔspxA1ΔsaiR +saiR(C96S) (ORB8724).
B. SaiR represses spxA2 transcription in B. subtilis. Open bars show spxA2-lacZ expression in the absence of SaiR (ORB8884), in the presence of wild-type SaiR (ORB8820), SaiR(C89S) (ORB8825), SaiR(C96S) (ORB8826), and SaiR(C89S C96S) (ORB9055). The spxA2 promoter contains the region between −247 and +268 relative to the spxA2 transcription start site. Gray bars show that the his6 tag has no effect on the activity of SaiR. Strains: wild-type saiR-his6 (ORB8985); saiR(C96S)-his6 (ORB9047); saiR(C89S C96S)-his6 (ORB9064).