Figure 1. Survivin is expressed in mouse HSC and disruption of Survivin impairs their function.
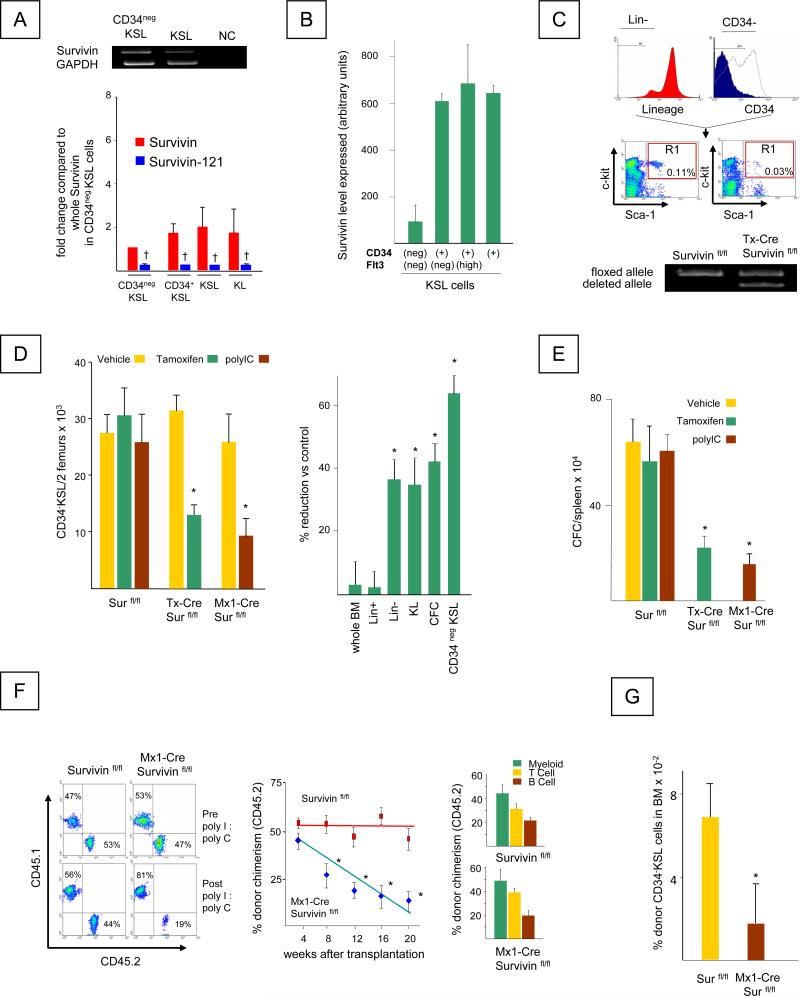
A. Left Panel, Top: RT-PCR for Survivin mRNAs in FACS sorted KSL and CD34negKSL bone marrow cells. GAPDH was used as an internal control. NC represents the negative control containing no template. Bottom: Quantitative analysis of wild-type Survivin and Survivin-121 in hematopoietic cell populations. † = significant reduction of Survivin-121 compared to full length Survivin in respective cell type, P<0.05.
B. Survivin expression in CD34neg Flt3 neg KSL, CD34pos Flt3 neg KSL, CD34pos Flt3 high KSL and CD34pos KSL cells from GSE 4322, (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo).
C. Top: Gating criteria for isolation of CD34neg KSL cells. Bottom: RT-PCR analysis for floxed and deleted Survivin alleles in Survivinfl/fl and CreER-Survivinfl/fl mice following Tamoxifen treatment. The data are representative of 3 independent experiments.
D. Left panel: The absolute number of CD34negKSL cells per 2 femurs in Survivinfl/fl and CreER-Survivinfl/fl and Mx1-Cre Survivinfl/fl mice before and after Survivin deletion, determined by multiplying the absolute total nucleated cell number in 2 femurs by the percentage of CD34negKSL cells. Data represent the mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05. Right panel: The percent reduction of total nucleated marrow cells, lineage+ cells (Lin+), lineage- (Lin-) cells, c-kit+ lin- (KL) cells, CFC (CFU-GM, BFU-E, CFU-GEMM) and CD34negKSL cells in bone marrow obtained from Tamoxifen treated CreER-Survivinfl/fl and Survivinfl/fl mice. Data are the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05
E. Mean total CFC/spleen ± SEM, in spleen of 3 individual mice, each assayed individually. *P<0.05
F. Left panel: Representative staining for nucleated peripheral blood CD45.1 and CD45.2 cells in recipient C57Bl/6 mice transplanted with donor (CD45.2) (Survivinfl/fl or Mx1-Cre Survivinfl/fl) and competitor cells (CD45.1) at a ratio of 1:1. Peripheral blood was harvested. Peripheral blood chimerism in the recipients receiving Survivinfl/fl marrow cells (left plots) or Mx1-Cre Survivinfl/fl marrow cells (right plots) at 4 weeks post-transplant prior to polyI:polyC injection (top) and at 20 weeks, 16 weeks after polyI:polyC injection (bottom).
Center panel: Donor (CD45.2) chimerism in the recipients transplanted with Survivinfl/fl marrow cells (red squares) or Mx1-Cre Survivinfl/fl marrow cells (blue diamonds) at 4 weeks post-transplantation prior to polyI:polyC treatment and at 4 week intervals thereafter. *P<0.05 (N=10).
Right panel: Tri-lineage analysis for donor derived (CD45.2) T, B and myeloid cells in recipient mice at 20 weeks post-transplant. Mean ± SEM; N= 10 mice/group, each assayed individually).
G. The frequency of CD34negKSL cells in the bone marrow of recipient mice was determined at 24 weeks post transplantation (20 weeks post polyI:polyC treatment). *P<0.05 (N=10)