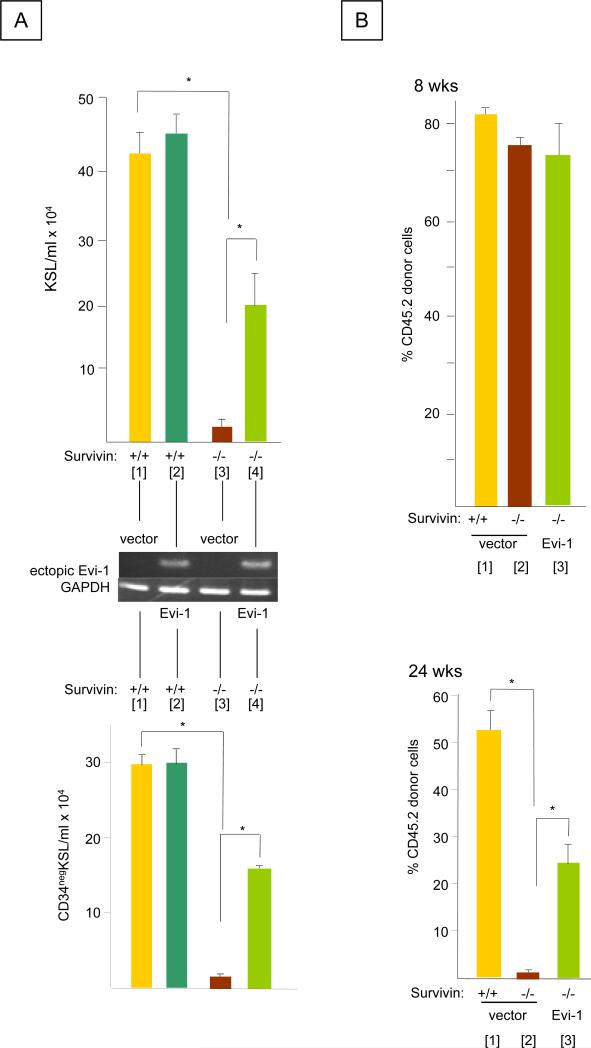
Figure 3. Effect of ectopic Evi-1 expression on the in vitro proliferation of CD34negKSL cells and the long-term repopulating activity of HSC lacking Survivin.
A. Bone marrow cells from CreER-Survivinfl/fl and control Survivinfl/fl were retrovirally transduced with MSCV (-) or MSCV containing human Evi-1 (19) and cultured with 100 ng/ml each of rhTpo, rmSCF and rhFL in 10% FBS/IMDM containing 1μM of 4OH-Tamoxifen for 7days. Top panel: KSL cells and Bottom panel: CD34negKSL cells were quantified by cell enumeration and flow cytometry (* P<0.05, N=3). Middle panel: Expression of ectopic human Evi-1 and GAPDH (as an internal control) determined by RT-PCR.
B. Peripheral blood chimerism in (CD45.1) recipients transplanted with (CD45.2) Mx1-Cre Survivinfl/fl cells expressing vector control or Evi-1or Survivinfl/fl marrow cells. PolyI:polyC was injected (i.p.) at 8 weeks post-transplantation. The proportion of CD45.2 cells before polyI:polyC injection (8 week, Top panel) and 24 weeks (Bottom panel) after polyI:polyC treatment are shown (*P<0.05 N=10).