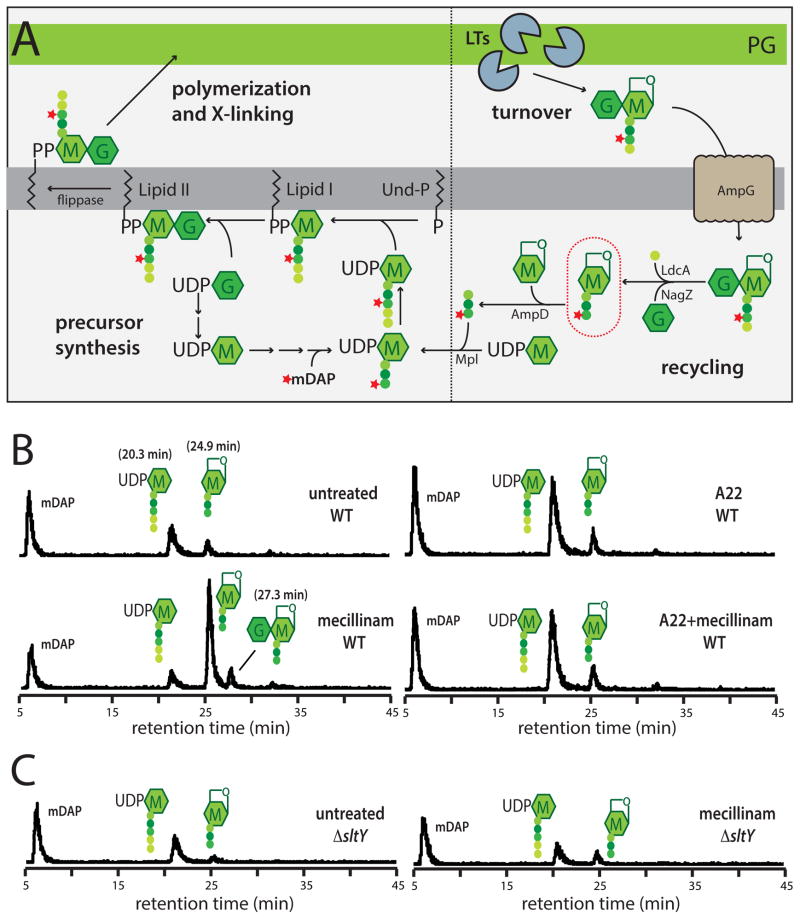
Figure 3. Measurement of PG synthesis and turnover following mecillinam treatment.
A. Schematic summarizes the PG synthesis and recycling pathways. Sugars and peptides are represented as in Figure 1A. The composition of the pentapeptide of the cytoplasmic precursors is L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-meso-diaminopimelic acid (mDAP)-D-Ala-D-Ala. UDP-sugars are first made in the cytoplasm before being transferred to the lipid carrier undecaprenol-phosphate (Und-P). The final precursor lipid II is the substrate used by the PBPs to form PG. As a result of the crosslinking mechanism and the activity of carboxypeptidase enzymes that remove the terminal D-Ala, the PG layer consists primarily of glycans with tetrapeptides. The turnover product circled in red will accumulate in a ΔampD strain if nascent PG is degraded during a pulse labeling experiment. See text for details. B–C. Measurement of PG synthesis and turnover by the Rod system. Cells of TU278 [ΔlysA ΔampD] (B) or its Δslt derivative (HC419) (C) producing SulA to block cell division were pulse labeled with [3H]-mDAP following treatment with the indicated drug(s) (10 μg/ml each when added). Soluble metabolites were separated by HPLC and detected using an in-line radiodetector. The resulting chromatograms are shown. Peaks are labeled with schematics of the corresponding compounds. The identity of each peak is based on the results shown in Figure S3. See text for details.