Fig. 5.
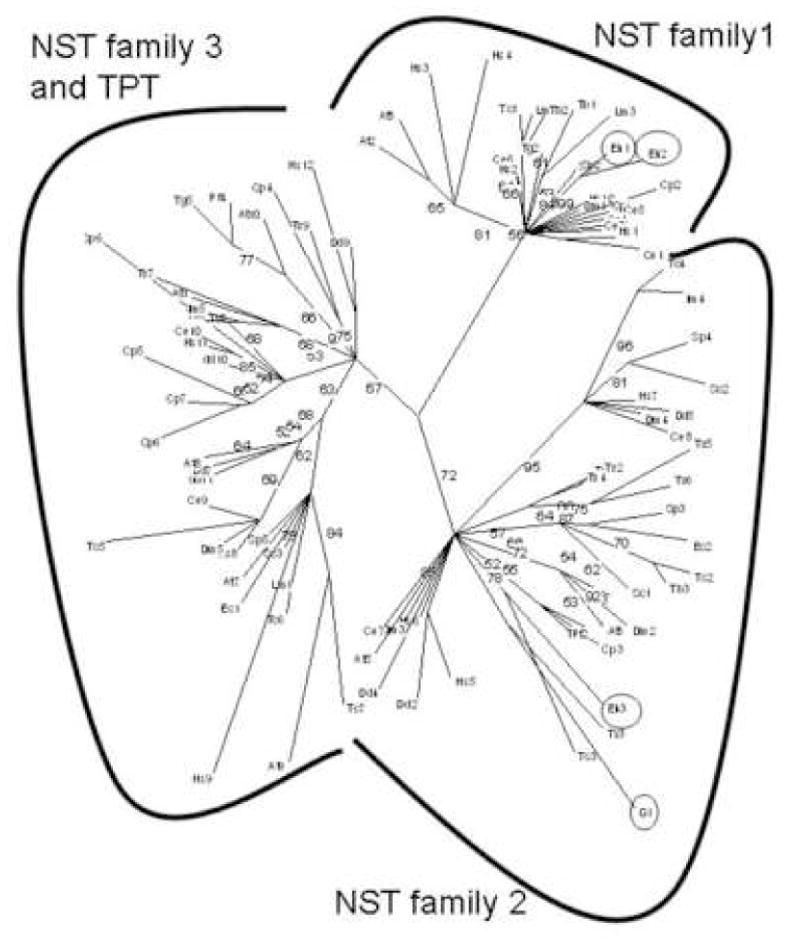
Phylogenetic tree of protist, fungal, and metazoan NSTs constructed by maximum likelihood method (21, 22). Protists include Giardia lamblia (Gl), Entamoeba histolytica (Eh), Trichomonas vaginalis (Tv), Trypanosoma cruzi (Tc), Trypanosoma brucei (Tb), Leishmania major (Lm), Plasmodium falciparum (Pf), Toxoplasma gondii (Tg), Cryptosporidium parvum (CP), and Dictyostelium discoideum (Dd). Fungi include Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc), Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp), and Encephalitizoon cuniculi (Ec), while metazoans include Homo sapiens (Hs), Caenorhabditis elegans (Ce), and Drosophila melanogaster (Dm). Arabidopsis thaliana (At) is the only plant. NCBI gene id numbers for each NST are listed in Supplemental Table 1. Giardia and Entamoeba NSTs are circled. Lengths of branches are proportional to differences between sequences, while numbers at nodes refer to bootstrap values for 100 trees. These bootstraps strongly support three distinct families of NSTs (3, 4).
