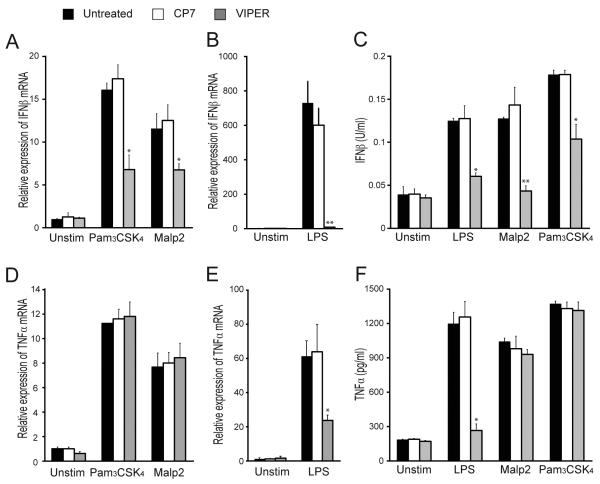
Figure 1. VIPER inhibits TLR2-dependent IFN-β induction.
(A, B, D, E) WT iBMDMs were treated with 5 μM VIPER or CP7 peptide 1 h prior to being stimulated with 20 nM Malp2, 20 ng/ml Pam3CSK4 or 100 ng/ml LPS for 3 h. Induction of IFN-β (A, B) and TNF-α (D, E) mRNA expression was assayed by quantitative RT-PCR, normalized to β-actin and presented relative to untreated, unstimulated cells. (C, F) Cells were treated as described above except TLR stimulations were for 24 h. Production of IFN-β (C) and TNF-α (F) protein was assayed by ELISA. For (A-F) the data are mean ± SD of triplicate samples and are representative of at least three independent experiments. *p<0.05, **p<0.005 or ***p<0.0005 compared to samples treated with control peptide (CP7).