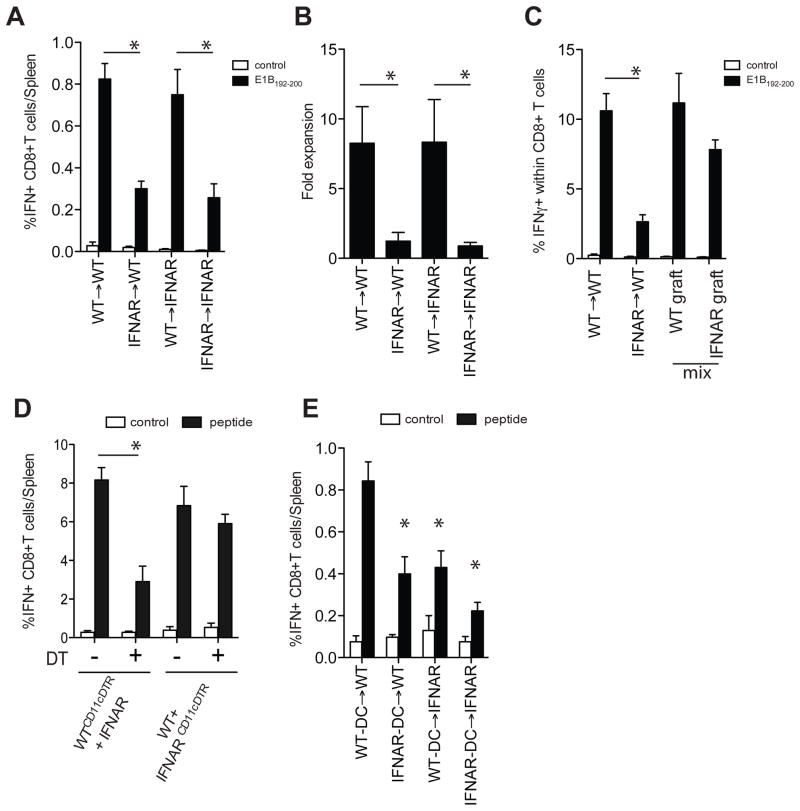
Figure 3. Selective requirement for type I IFN sensing in the DCs.
A. Bone-marrow chimeric mice (WT→IFNAR−/−, WT→WT, IFNAR−/−→WT, IFNAR−/−→IFNAR−/−) were immunized i.p. with irradiated 5E1-TAKO cells and the frequency of E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells in the spleens was determined 7 days later (white bar, control peptide; black bar, E1B192-200 peptide). B. The effect on memory formation using these chimeras was determined by measuring antigen-specific T cell expansion ex vivo. Secondary expansion of E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells was calculated by dividing the absolute number of E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells at the end of a6 day culture by the absolute number at the start of the culture. C. WT/CD90.1 mice were irradiated and reconstituted with WT, IFNAR−/− or a 1:1 ratio of WT (CD45.1):IFNAR−/−(CD45.2) bone-marrow. Mice were i.p. immunized with irradiated 5E1-TAKO cells and the frequency of splenic E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells in each graft was determined 7 days later. D. WTCD11cDTR:IFNAR−/− and WT:IFNAR−/−CD11cDTR mixed bone-marrow chimeras were treated with DT or vehicle and immunized with irradiated 5E1-TAKO cells. The frequency of E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells in the WT compartment was determined 7 days later. E. Freshly isolated WT and IFNAR−/− DCs were incubated with irradiated 5E1-TAKO cells, sorted and i.v. injected into WT and IFNAR−/− mice. The frequency of splenic E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells was determined 7 days later. Data of representative experiments (out of 3–5) are shown (mean± s.e.m, n=5/group).