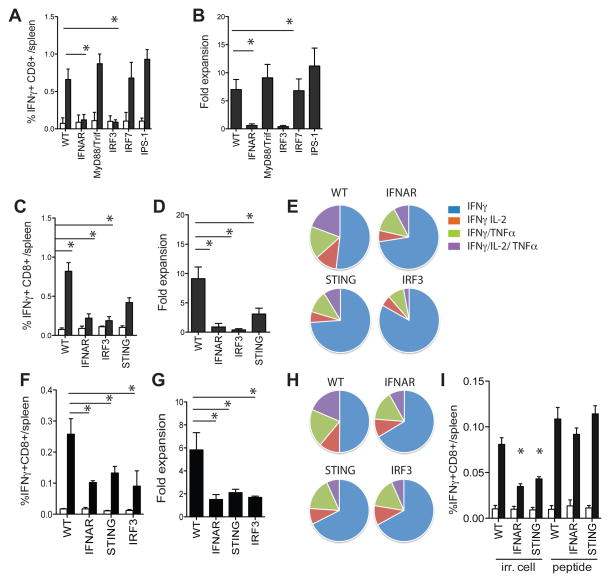
Figure 7. STING regulates the CD8+ T cells responses to dying cells in vivo.
A. Mice of indicated strains were immunized with irradiated 5E1-TAKO cells and the frequency of splenic E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells was determined 7 days later (white bar, control peptide; black bar, E1B192-200 peptide). B. Fold expansion of E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells from indicated mouse strains upon culture with E1B192-200-expressing feeder cells in vitro. C. E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cell frequency in indicated mouse strains 7 days after immunization with irradiated 5E1-TAKO cells. D. Secondary expansion of E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells in vitro. E. Ex vivo polyfunctionality of E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells from fig C as determined by flow cytometry. F. Frequency of E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells in WT mice 7 days after transfer of indicated DCs pulsed with irradiated 5E1-TAKO cells in vitro. G. Secondary expansion of E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells primed by indicated DCs. H. Ex vivo polyfunctionality of E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells primed by indicated DCs. I. DCs were purified from WT, IFNAR−/− and STING−/− mice and exposed to irradiated 5E1-TAKO cells or pulsed with 1uM E1B192-200 peptide. DCs were repurified and 2 × 105 were injected into WT recipients. Seven days later the frequency of splenic E1B192-200-specific CD8+ T cells was determined (white bar, control peptide; black bar, E1B192-200 peptide). Representative data of one experiment (of 3–4) are shown (mean± s.e.m., n=5–7).