Figure 6.
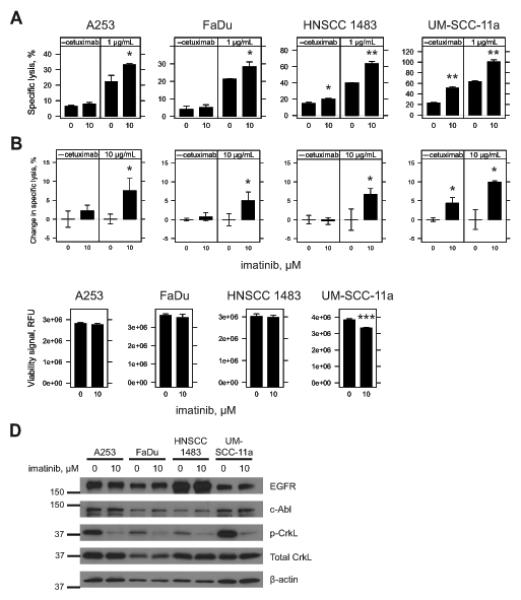
Inhibition of c-Abl kinase activity by imatinib and sensitivity of HNSCC cell lines to ADCC. A & B, A253, FaDu, HNSCC 1483 and UM-SCC-11a cells were seeded overnight in 96-well plates and treated for 48 h with vehicle (0, DMSO) or imatinib (10 μM). Treatments were aspirated and replaced with fresh growth media just prior to addition of effector cells in the absence or presence of cetuximab. Cytotoxicity was assessed 4 h later and specific lysis was determined. For A, 40,000 NK92-CD16V cells were used in the absence or presence of 1 μg/mL cetuximab. For B, 50,000 IL2 negatively-selected, IL2 stimulated NK effector cells were used in the absence or presence of 10 μg/mL cetuximab. Percent change in specific lysis was quantified to account for varying levels of donor specific lysis against target cells. Results represent one of two independent experiments using three independent donors (n=3). C, A253, FaDu, HNSCC 1483 and UM-SCC-11a cells were seeded overnight in 96-well plates and treated for 48 h with vehicle (0, DMSO) or imatinib (10 μM). Viability was assessed by fluorometric assay. For A, B and C, imatinib pre-treatment was compared to vehicle control within each sub-panel. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; and ***, p<0.001 by two-tailed t-test. Results are from three independent experiments (n=3) for each cell line. Error bars represent s.d. of the mean. D, A253, FaDu, HNSCC 1483 and UM-SCC-11a cells were seeded in six-well plates overnight and treated for 48 h with vehicle (0, DMSO) or imatinib (10 μM). Cell lysates were collected and Western blots were conducted. c-Abl was blotted before stripping and re-blotting for EGFR. Phospho-CrkL (p-CrkL) was blotted for before re-blotting for both total CrkL and then β-actin as a loading control. Densitometry was conducted and relative expression was assessed within each cell line for vehicle and imatinib treatments (Supplementary Fig. 6C). Results are representative of two independent experiments.
