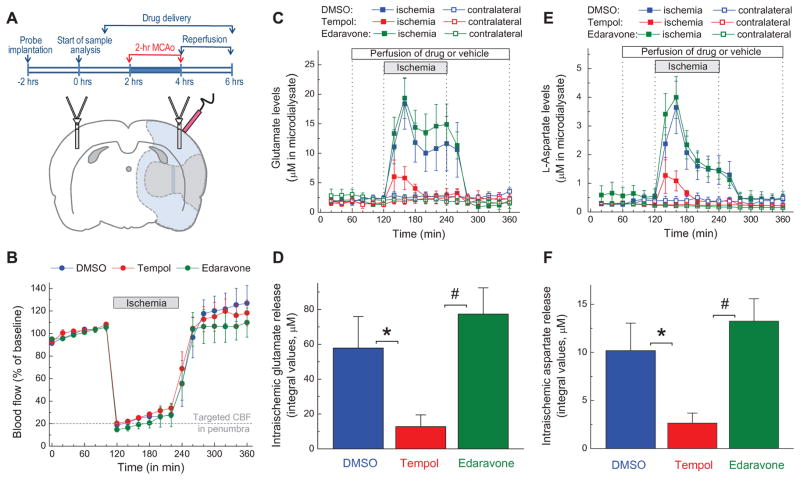
FIG. 1. Effects of the antioxidants tempol and edaravone on microdialysate levels of glutamate and aspartate in rat cortex before, during and after transient occlusion of the middle cerebral artery (MCAo).
A, Experimental design and schematic representation of position of microdialysis probes and laser Doppler probe in the MCAo experiments. Shaded gray (inner area) and light blue (outer area) regions approximately correspond to the ischemic core and penumbra, respectively. B, Dynamics of cerebral blood flow (CBF) in all three experimental groups. CBF was quantified using a laser Doppler probe and then normalized to the average CBF values before MCAo. C, Microdialysate levels of glutamate on ischemic and non-ischemic (contralateral) sides of the brain. Vehicle (2% DMSO), 10 mM tempol, or 10 mM edaravone were added into the aCSF as indicated. The data are the mean values ±SE in 9–10 animals per group. D, Integral values of the intra-ischemic glutamate release in the experiments presented in C. *p<0.05, DMSO vs. tempol; #p<0.05, tempol vs. edaravone. E, Microdialysate levels of aspartate on ischemic and contralateral sides of the brain. n= 9–10 per group. F, Integral values of intra-ischemic aspartate release in the experiments presented in E. *p<0.05, DMSO vs. tempol; #p<0.05, tempol vs. edaravone.