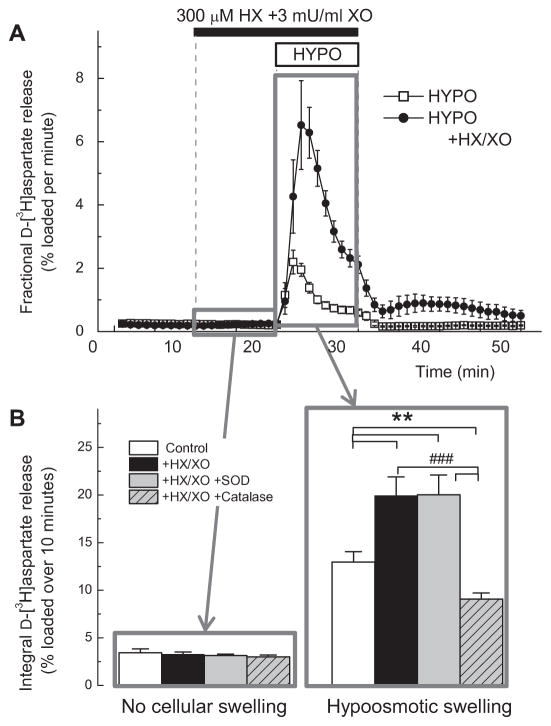
FIG. 6. Hydrogen peroxide but not superoxide anion potently stimulates glutamate release in primary astrocyte cultures.
A, Kinetics of D-[3H]aspartate release from primary astrocytes superfused with the mix of 3 mU/mL xanthine oxidase (XO) and 300 μM hypoxanthine (HX), which produces both O2•− and H2O2. To mimic pathological swelling, cells were additionally exposed to hypoosmotic medium (HYPO, 30% reduction in medium osmolarity). n=5–6. ***p<0.001, HYPO vs. HYPO in combination with HX+XO. B, The nature of ROS contributing to stimulation of D-[3H]aspartate release was tested by adding SOD (200 U/ml), or catalase (15 μG/mL). The integral release values during 10-min periods either prior to cellular swelling (11th–20th min), or during swelling (21st–30th min) were measured as described in Materials and Methods. n= 5/group. *p<0.05, vs. HYPO alone; ###p<0.001, HYPO + catalase vs. HYPO+X/XO, or HYPO+HX/XO+SOD.