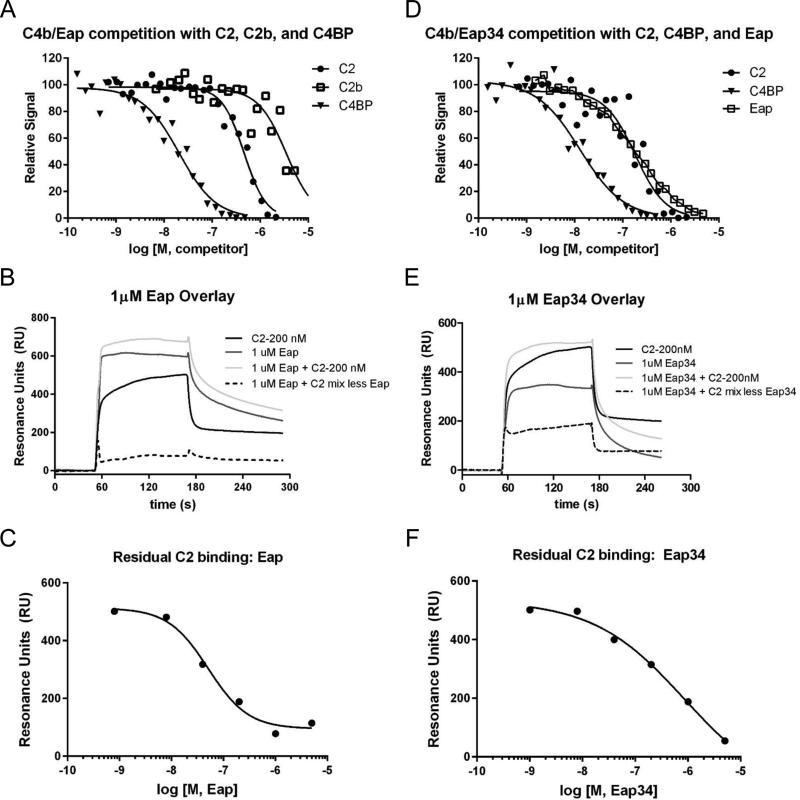
Figure 5. Eap Binding Inhibits the Interaction of Complement Component C2 with C4b.
(a) The ability of recombinant human C2, C2b, and C4BP to compete the AlphaScreen signal generated by myc-Eap and C4b-biotin was assessed over a logarithmic dilution series. While three independent trials were carried out, the data presented here are from a single representative titration. The smooth line indicates the outcome of fitting all points to a dose-response curve. (b) Representative data from an SPR competition experiment where the effect of 1 μM Eap on the interaction of 200 nM C2 with a C4b-biotin surface was examined. A legend showing the identity of each sensorgram is inset. The residual C2 binding in the presence of Eap is shown as a dashed line, while the sensorgram for the same concentration of C2 in the absence of any Eap is shown as the darkest black line. (c) Residual C2 binding in the presence of various concentrations of Eap fit to a dose-response curve (IC50 = 50 nM). (d) Identical experiment to panel a, with the exception that the ability of recombinant human C2, C4BP, and Eap to compete the AlphaScreen signal generated by myc-Eap34 and C4b-biotin was assessed. (e) Identical experiment to panel b, with the exception that Eap34 was used as the competitor instead of Eap. The residual C2 binding in the presence of Eap34 is shown as a dashed line, while the sensorgram for the same concentration of C2 is shown as the darkest black line. (f) Residual C2 binding in the presence of various concentrations of Eap34 fit to a dose-response curve (IC50 = 870 nM).