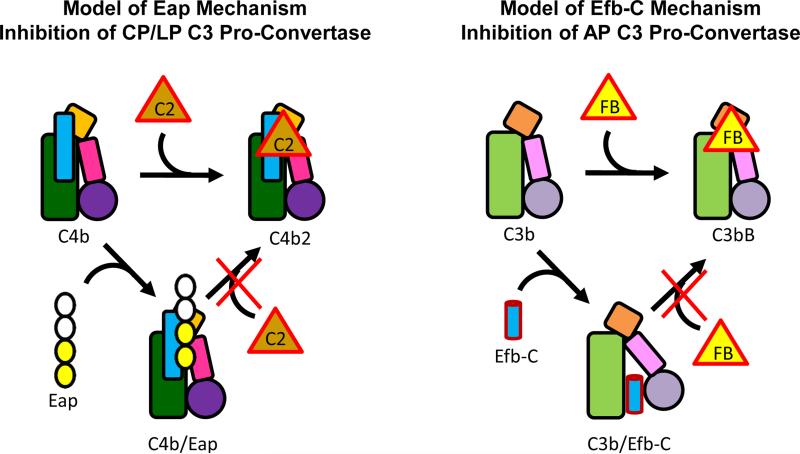
Figure 6. Proposed Mechanism for Eap-mediated Inhibition of the CP/LP C3 and Its Similarities to the S. aureus AP Inhibitor, Efb-C.
The overall structural similarities between C4b and C3b are represented by the similar shapes of their cartoon representations. The shaded green rectangle represents the macroglobulin-like core, the orange square the C345C domain, the small pink rectangle the CUB domain, and filled circle the thioester-containing domain (i.e. C4d and C3d). The thin blue rectangle represents the γ-chain unique to C4/b. The inhibitor Eap is shown in the left panel with two domains filled in yellow to represent the domains 3 and 4 ‘active site’, as described in Figs. 4 and 5. The inhibitor Efb-C is shown as a blue cylinder in the right panel. Efb-C binding to the C3d domain (45) and stabilization of an open, inactive conformation of C3b that is unable to bind FB (10) is depicted by reorientation of the CUB-TED region relative to the macroglobulin-like core of C3b.