Figure 1.
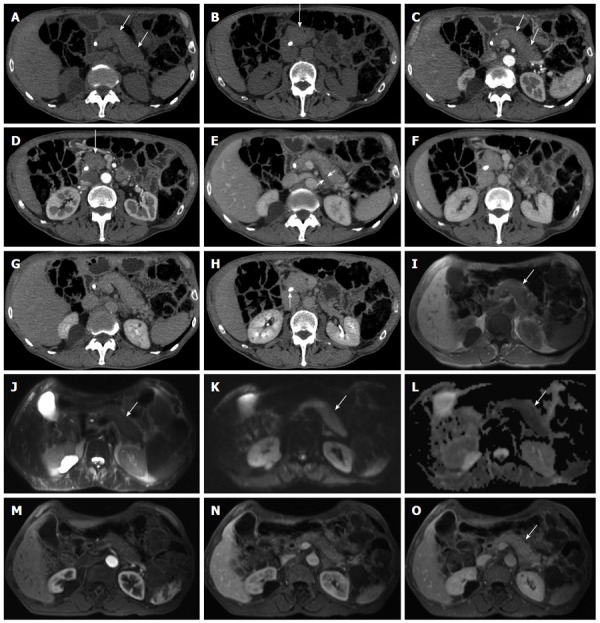
Diffuse-type autoimmune pancreatitis. A-H: Computed tomography: the pancreas appears diffusely enlarged (arrows in A-D) with a hypodense peripancreatic rim, better visible in the venous phase (arrow in E). The lesion shows fair enhancement resulting almost isodense in the delayed phase (G-H). A plastic biliary endoprothesis is visible in the common bile duct (arrow in H); I-O: Magnetic resonance: the entire organ is slightly hypointense on T1-weighted images (arrow in I) and slightly hyperintense on T2-weighted images (arrow in J), with diffusion coefficient restriction (arrows in K and L) with intermediate-high b values. At dynamic examination the pancreatic lesion presents fair enhancement resulting almost isodense in the delayed phase (arrow in O).
