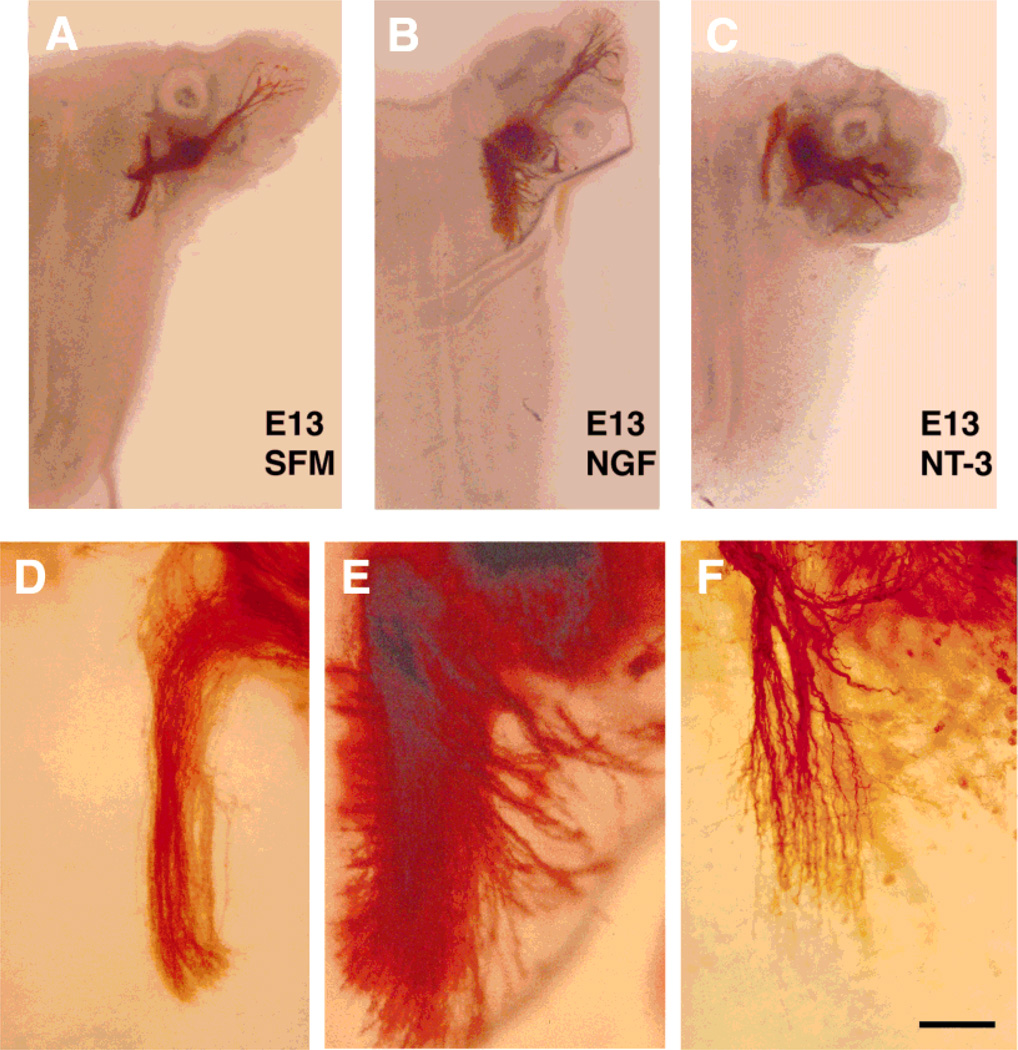
Fig. 4.
Effects of neurotrophins on embryonic day (E)13 central trigeminal axons. Low-power photomicrographs of E13 wholemount cultures of intact whisker pad-trigeminal ganglion (TG)-brainstem explants (A–C). As in E15 cases, central trigeminal axons remained unbranched in cultures grown in serum-free culture medium (SFM; A and D). In nerve growth factor (NGF)-treated cultures (B and E), descending trigeminal tract expanded and dense axon fascicles diverged from the central tract into the brainstem parenchyma. In neurotrophin-3 (NT-3)-treated cultures (C and F), axons formed short collateral branches some with rudimentary arbors. Scale bar = 500 µm in A–C; 150 µm in D–F.