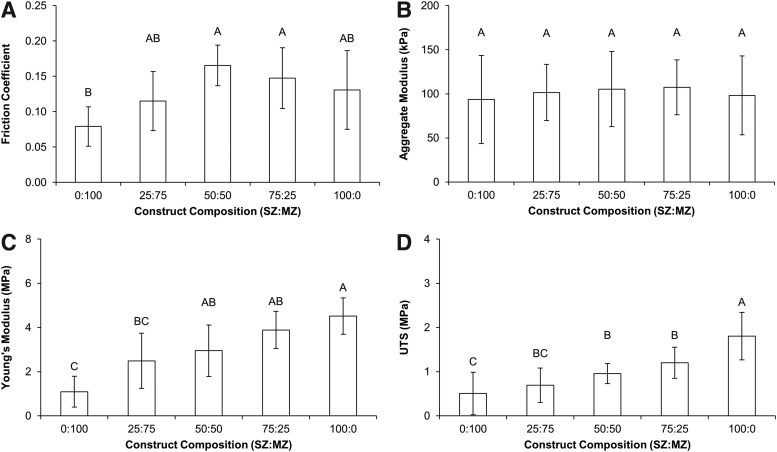
FIG. 3.
Biomechanical properties of constructs after 4 weeks of culture. The boundary mode friction coefficient (A), aggregate modulus (B), Young's modulus (C), and ultimate tensile strength (D) of the constructs were measured. The friction coefficient of engineered constructs was significantly lowest in the 100% MZ constructs. There were no significant differences in frictional properties between the other construct groups. The friction coefficient of 100% MZ constructs approached the value of native MZ articular cartilage. There were no statistically significant differences between constructs in the compressive mechanical properties measured. However, tensile properties were enhanced in constructs composed of greater proportions of SZ chondrocytes. Values are presented as mean±SD.