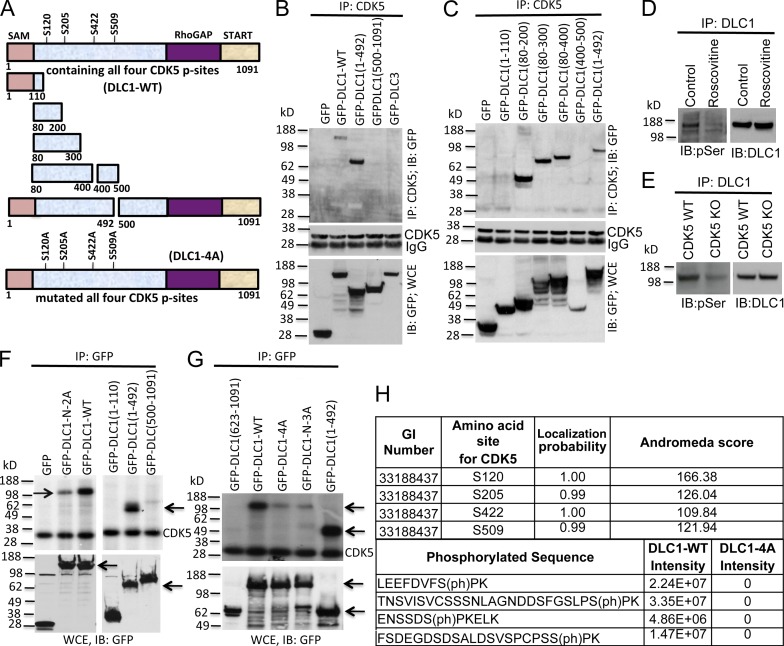
Figure 2.
Mapping the DLC1 region required for CDK5 binding; four serines in DLC1 are CDK5 substrates. (A) Schematic representation of full-length WT DLC1 with the location of four serines phosphorylated by CDK5 (DLC1-WT), various DLC1 fragments, and DLC1-4A mutant with the four CDK5 serines mutated to alanine. All constructs were GFP tagged. (B) DLC1 amino acids 1–492 are sufficient for complex formation between DLC1 and CDK5. (B, top) Lysates of 293T cells transfected with the indicated DLC1 construct were immunoprecipitated with CDK5 antibody followed by IB with GFP antibody. (B, middle) IP reaction to show the equal IP for CDK5 protein. (B, bottom) Expression of transfected DLC1 constructs. (C) DLC1 amino acids 80–200 are necessary and sufficient for complex formation between DLC1 and CDK5. Experimental conditions and data display are as in B, except that we used smaller DLC1 fragments to map the minimal DLC1 fragment required for CDK5 binding. (D) Roscovitine treatment of H1703 cells reduces serine phosphorylation (pSer) of DLC1 (left) without reducing the level of DLC1 (right). (E) DLC1 from CDK5−/− MEFs has less phosphoserine (pSer) than DLC1 from WT MEFs (left), while the DLC1 level is unchanged (right). (F) In vitro CDK5 kinase assay. (top) Immunoprecipitated DLC1-WT was strongly phosphorylated by recombinant CDK5 (left, top arrow), as detected with 32P autoradiography. DLC1-N-2A mutant (with an S-to-A mutation of S120 and S205) is less strongly phosphorylated (left, top arrow). DLC1(1–492) is strongly phosphorylated (right, bottom arrow). (bottom) Expression of GFP, GFP-DLC1-WT, and GFP-DLC1 fragments. (G, top) In vitro phosphorylation signal by recombinant CDK5 depends on the number of Serines present in WT and mutant DLC1 fragments (top arrow). DLC1-N-3A has S-to-A mutations of S102, S205, and S422. DLC1(1–492) is a positive control (bottom arrow). (G, bottom) Expression of GFP and GFP-tagged DLC1 constructs (top arrow) and DLC1(1–492) (bottom arrow). (H) Phosphorylation of DLC1 by CDK5. DLC1 phosphopeptides were detected by mass spectrometry. All CDK5 phosphorylation sites were fully localized to the indicated serine residues, and were absent from the DLC1-4A mutant protein. See also Figs. S2 and S3.