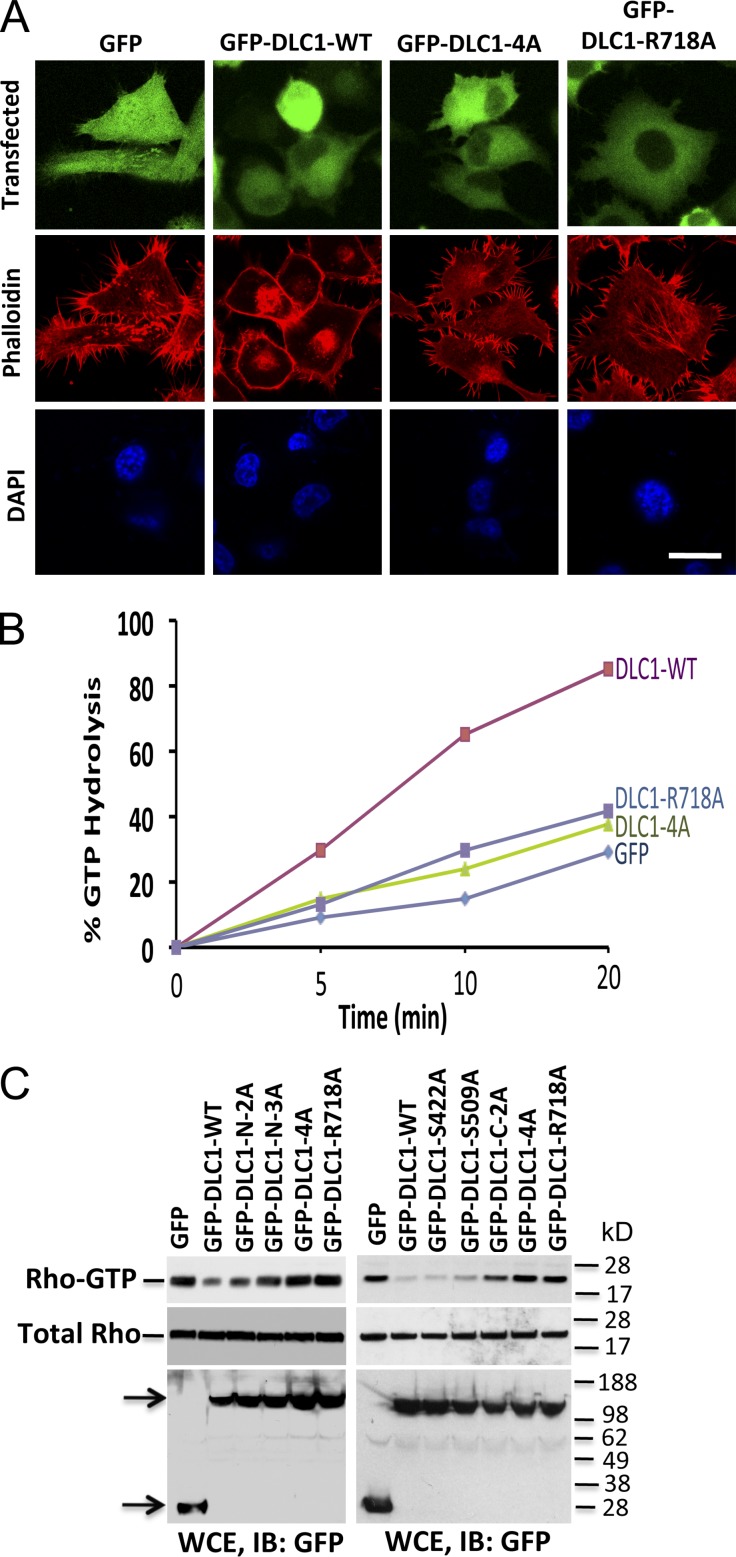
Figure 5.
Rho-GAP activity of DLC1 is inversely related to the number of S-to-A mutations in DLC1. (A) H358 cells transfected with GFP, GFP-WT-DLC1, GFP-DLC1-4A, or GFP-DLC1-R718A mutants were immunostained with phalloidin (red). Cells transfected with GFP-DLC1-WT show fewer stress fibers. In contrast, cells transfected with GFP-DLC1-4A mutant show almost identical morphology as “GAP-dead” GFP-DLC1-R718A or GFP-negative control for stress fibers formation. DAPI (blue) represent nuclei. The confocal images are representative of the majority of cells. Bar, 20 µm. (B) In vitro GTP hydrolysis of RhoGTP was significantly increased by GFP-DLC1-WT compared to GFP alone, GFP-DLC1-4A, or “GAP-dead” GFP-DLC1-R718A mutant. Unlike the GFP-DLC1-WT–positive control, GFP-DLC1-4A mutant is as defective as “GAP-dead” mutant for Rho-GAP activity. (C) RhoGTP (top) and total Rho (middle) in individual or combined mutants of DLC1 in DLC1-negative A549 cells. The RhoGTP levels are inversely related to the number of S-to-A mutations, and the degree of Rho-GAP reduction is additive for each mutation. Expression of indicated DLC1 constructs was detected by GFP antibody in WCE (bottom). Arrows indicate the expressed proteins.