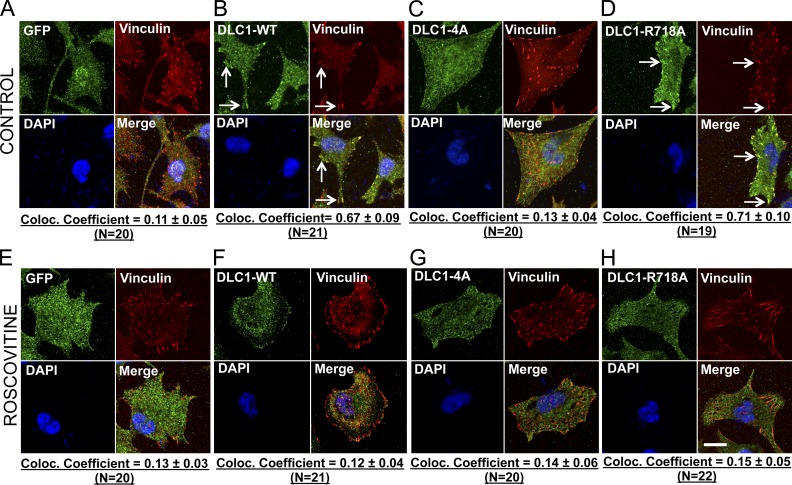
Figure 8.
The closed conformation of DLC1-4A affects its subcellular localization. (A–D) Colocalization of GFP-tagged DLC1 constructs (green) with the focal adhesion protein Vinculin (red). Unlike the stable GFP control in H1703 cells (A), the stable DLC1-WT (B) and “GAP-dead” DLC1-R718A (D) efficiently colocalize to focal adhesions. In contrast, DLC1-4A mutant poorly colocalizes to focal adhesions (C). (E–H) Experimental conditions were similar to as above, except that cells were treated with Roscovitine. Treatment with Roscovitine changes the subcellular localization of DLC1-WT and “GAP-dead” DLC1-R718A proteins away from focal adhesions so that they no longer colocalize with focal adhesions, which appears similar to DLC1-4A mutant protein. The images are representative of a majority of cells. An averaged overlapping colocalization coefficient ± SD was calculated from 18–22 cells per condition randomly selected from several fields, and is shown at the bottom of each panel. Bar, 20 µm.